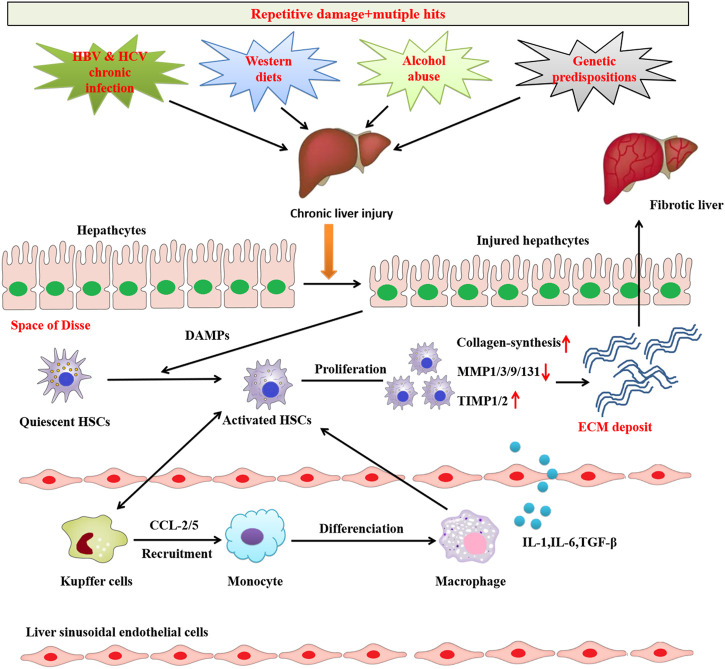
FIGURE 1.
Common mechanisms of liver fibrosis. Repetitive damage and mutiple hits causes chronic hepatocyte injury, which causes release of damage-associated patterns (DAMPs) that activate Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and recruit immune cells. Activated HSCs are continuously activated and proliferated to secret abundant fibrogenic cytokines and produce excessive ECM, which causes the imbalance of pro-fibrosis/anti-fibrosismechanism.The pro-fibrosis mechanism leads to the abnormal formation of scar and eventually induces liver fibrosis.