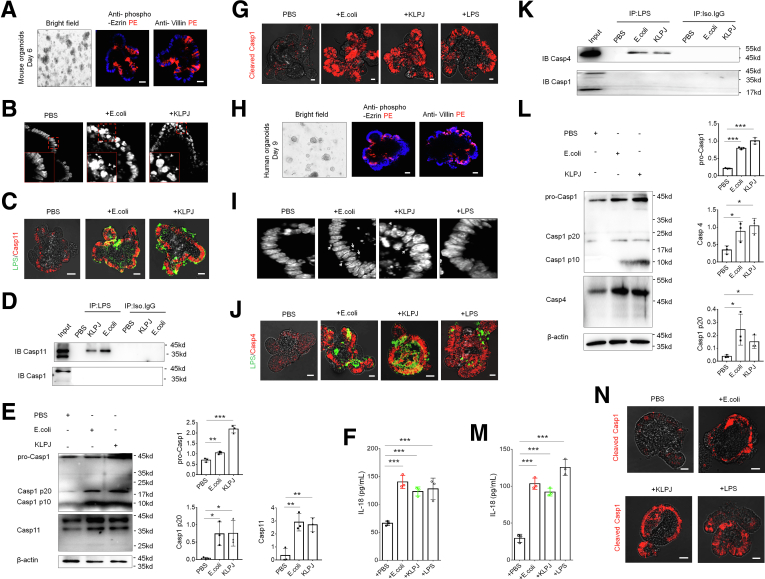
Figure 10.
KLPJ-mediated colitis is through binding of LPS from KLPJ with caspase-11 in the colonic epithelial cells. (A) Staining of mouse gut organoids (6 days) using anti–phospho-ezrin or villin. (B) E coli and KLPJ under a light microscope in gut organoids. Arrow indicates E coli or KLPJ. (C) Fluorescence microscope of the binding of LPS and caspase-11 in gut organoids. (D) Immunoprecipitation using biotin-labeled LPS, and then immunoblotting using anti–caspase-11 or anti–caspase-1 antibody in the lyses of KLPJ–infected gut organoids. (E) Immunoblotting of pro-caspase 11 and mature caspase-11, and pro- and mature caspase-1 in the lyses of KLPJ or E coli–infected gut organoids. (F) ELISA of IL18 in the supernatants of KLPJ, E coli–infected gut organoids. LPS indicates control. (G) Staining of cleaved caspase-1 (cleaved casp-1) in KLPJ or E coli–infected gut organoid. LPS indicates control. (H) Staining of human gut organoids (9 days) using anti–phospho-ezrin or villin. (I) E coli and KLPJ under a light microscope in human colon organoids. Arrows indicates E coli or KLPJ. LPS indicates control. (J) Fluorescence microscope of the binding of LPS and caspase 4 in human colon organoid. LPS indicates control. (K) Immunoprecipitation using biotin-labeled LPS, and then immunoblotting using anti–caspase-4 or anti–caspase-1 antibody in the lyses of KLPJ–infected human colon organoid. (L) Immunoblotting of mature caspase-4 and pro- and mature caspase-1 in the lyses of KLPJ or E coli–infected human colon organoids. (M) ELISA of IL18 in the supernatant of KLPJ or E coli–infected human colon organoids. (N) Staining of cleaved caspase-1 (cleaved casp-1) in KLPJ or E coli–infected human colon organoids. For the entry and organoid immunofluorescence staining of KLPJ, microinjections were performed. For stimulation of KLPJ on gut organoids, the suspension of gut organoids was prepared. Student t test. Scale bars: 40 μm. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001. IB, immunoblotting; IP, immunoprecipitation; Iso,Isotype control.