Figure 10.
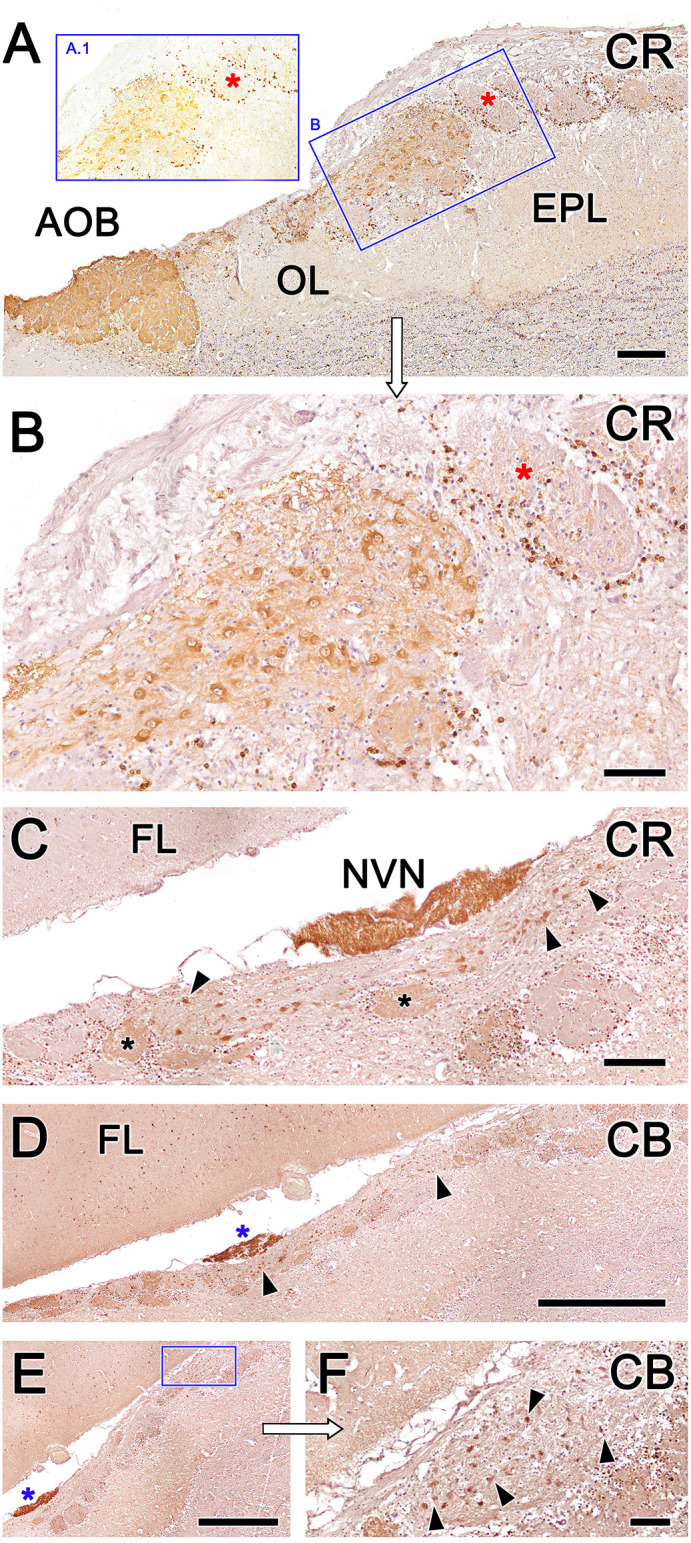
Fox olfactory limbus (OL) sections immunolabeled with the calcium-binding proteins calretinin (CR) and calbindin (CB) and counterstained with hematoxylin. (A) Anti-CR immunostaining produces intense labeling in the macroglomerular complex (MGC) of the OL (box B) and in the accessory olfactory bulb (AOB). The glomeruli of the main olfactory bulb (MOB) do not show any immunolabeling in their neuropil (red asterisks), although their periglomerular cells are clearly labeled, which is particularly evident in non-counterstained sections (box A.1). (B) A higher magnification image of box (B) from panel (A). In the MGC, both neuronal somata and the neuropil (asterisk) are immunolabeled with anti-CR. (C) Section at the level of the vomeronasal nerve (NVN) shows intense anti-CR immunopositivity. The atypical nervous formation beneath the NVN is elongated and contains scattered neuronal somata (arrowheads). A subpopulation of glomeruli is CR-positive (asterisks). (D) Anti-CB immunostaining produces a similar pattern to anti-CR immunostaining. The NVN is intensely immunopositive to anti-CB (blue asterisk). The MGC is delimited by arrowheads. (E) Atypical glomeruli are variably labeled with anti-CB. (F) Higher magnification of the inset in (E). Somata belonging to the MGC are intensely stained (arrowheads). AOB, accessory olfactory bulb; OL, olfactory limbus; EPL, external plexiform layer; FL, the frontal lobe of the telencephalon; NVN, vomeronasal nerve Scale bars: (D,E): 1 mm. (A,C): 250 μm. (B,F): 100 μm.
