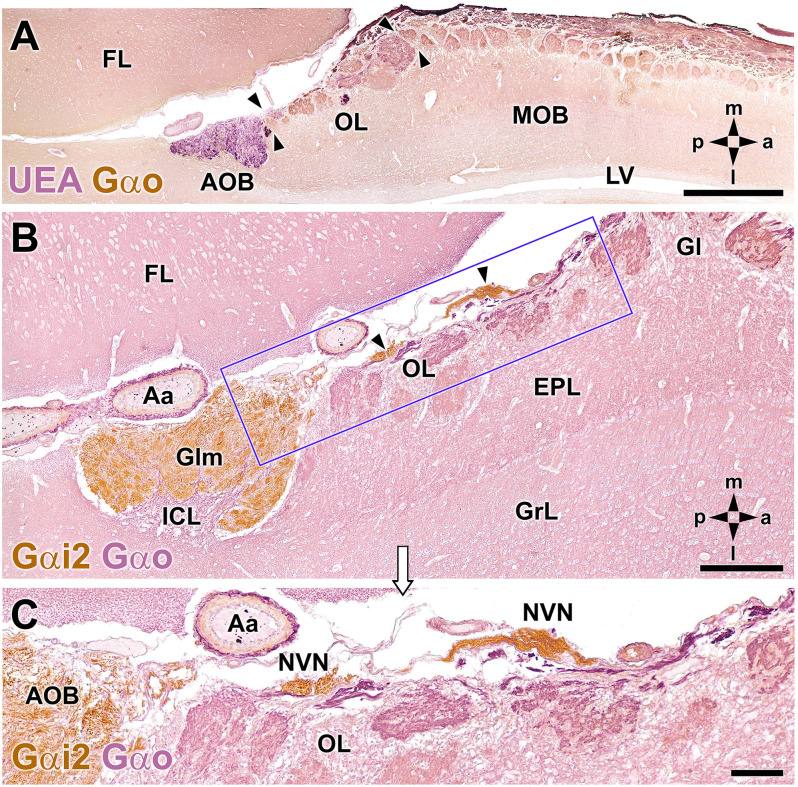
Figure 2.
Double-immunohistochemical labeling of the fox olfactory limbus (OL). (A) Double immunostaining with Ulex europaeus agglutinin (UEA) lectin (magenta) and Gαo antibody (brown). The vomeronasal nerve and glomerular layers of the accessory olfactory bulb (AOB) are strongly labeled with UEA. Anti-Gαo immunolabeling shows a widespread immunopositive pattern, more intensely in both the olfactory nerve and glomerular layers of the MOB. The OL, delimited by arrowheads, comprises irregularly shaped glomeruli, without a homogeneous immunostaining pattern. (B,C) Double immunostaining for Gαi2 (brown) and Gαo (magenta). Anti-Gαi2 stains the superficial AOB and the nervus vomeronasalis (NVN, arrowheads). Anti-Gαo stains the internal cellular layer (ICL) of the AOB and the neuropil of the olfactory bulb. The box in (B) is enlarged in (C), showing that the OL comprises irregularly shaped glomeruli without a homogeneous immunostaining pattern. The branches of the NVN, which are Gαi2-immunopositive, contrast with the Gαo-immunopositive nerve endings that project to the OL glomeruli. Aa, artery; EPL, external plexiform layer; FL, frontal lobe; Gl, MOB glomerular layer; Glm, AOB glomerular layer; GrL, MOB granular cell layer; LV, lateral ventricle. The compass indicates the orientation, as follows: m, medial; l, lateral; p, posterior; a, anterior. Scale bars: (A): 1 cm. (B,C): 250 μm.