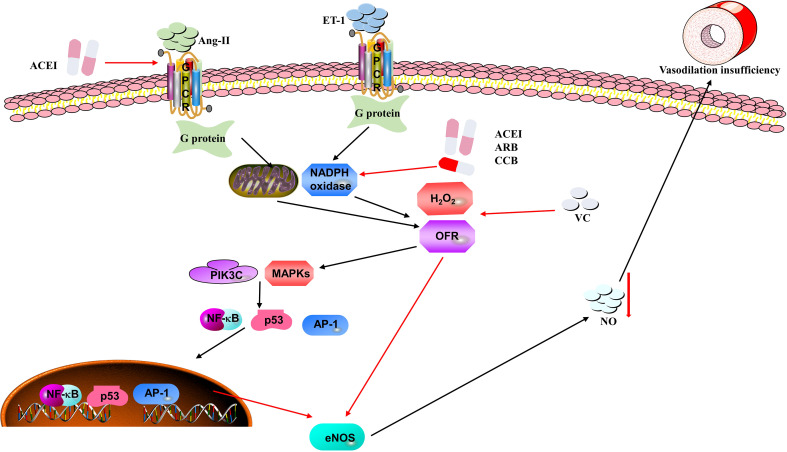
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of oxidative stress causing hypertension in vascular endothelial cells. Ang II and ET-1 can stimulate NADPH oxidase and mitochondria to produce ROS (e.g., H2O2 and OFR), which are recognized by their receptors on the endothelial cells. ROS stimulate the PI3K/Akt-MAPK pathway to inhibit the expression of eNOS mRNA and eNOS activity, thus reducing the availability of NO, which results in vasodilation insufficiency and elevation of blood pressure. Moreover, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers (CCBs) and vitamin C (VC) may be potential therapeutic strategies in the process of oxidative stress.