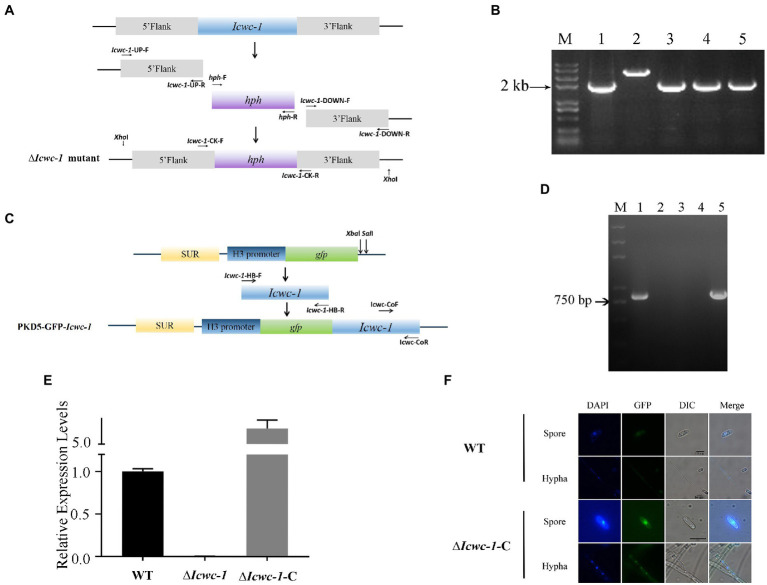
Figure 2.
Generation and identification Icwc-1 mutants of I. cicadae. (A) Schematic diagram of knockout ∆Icwc-1 via homologous recombination. (B) PCR validation of knockout strains. M: Maker, 1: knockout vector PCAMBIA1300-Icwc-1, 2: WT strain, 3–5: mutants. 3: ∆Icwc-1-2, 4: mutant ∆Icwc-1-8, 5: mutant ∆Icwc-1-40. (C) Schematic diagram of the generation of the complemented vector. H3 promoter in pKD5-GFP derived from Pyricularia oryzae. (D) PCR verification of complementary strains. M: Maker, 1: wild type strain WT, 2: mutant strain ∆Icwc-1-2, 3: mutant strain ∆Icwc-1-8, 4: mutant strain ∆Icwc-1-40, 5: the complementary strain ∆Icwc-1-C. (E) Expression of Icwc-1 gene in wild-type strain, mutant strain, and the complementary strain. (F) Location of Icwc-1 gene expression analysis. GFP observation under fluorescence microscope. The hyphae and spores of the wild-type strain and the ∆Icwc-1-C strain were stained with DAPI and observed under a fluorescence microscope. Bar = 10 μm.