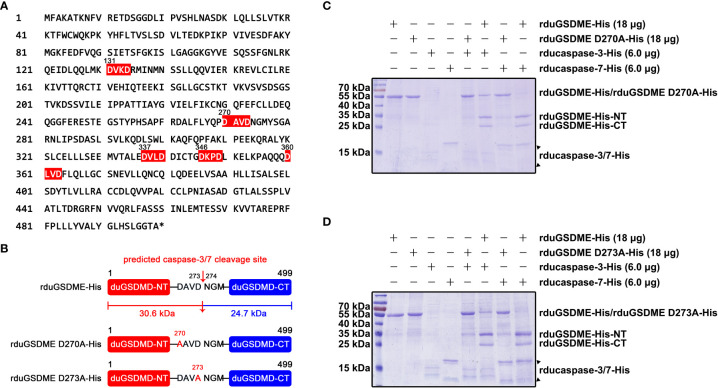
Figure 6.
Determination of the cleavage site(s) recognized by ducaspase-3 and ducaspase-7 in duGSDME molecules. (A) Potential recognition and cleavage sites of caspase-3 and caspase-7 in duGSDME molecules. The motifs in duGSDME molecules with the composition of D-x-x-D (D infers aspartate, x infers any amino acid residue) are considered the potential cleavage sites recognized by ducaspase-3 and ducaspase-7 and marked by red. The * indicates the end of the primary structure of duGSDME. (B) Structure models of rduGSDME D270A-His and rduGSDME D273A-His mutants. In the two mutants, the D270 or D273 of the duGSDME molecule was replaced with an alanine, respectively. The two aspartates are the components of the predicted cleavage site of ducaspase-3 and ducaspase-7. The two cleavage products of duGSDME by ducaspase-3 and ducaspase-7 from the predicted site are 30.6 kDa and 24.7 kDa in their molecular weights, respectively. (C) The affection of the D270A mutation to the cleavage of duGSDME by ducaspase-3 and ducaspase-7. The D270A mutation completely abolished the cleavage of rduGSDME-His by rducaspase7-His and rducaspase-7-His according to the SDS-PAGE gel. (D) The affection of the D273A mutation to the cleavage of duGSDME by ducaspase-3 and ducaspase-7. The D273A mutation completely abolished the cleavage of rduGSDME-His by rducaspase7-His and rducaspase-7-His according to the SDS-PAGE gel.