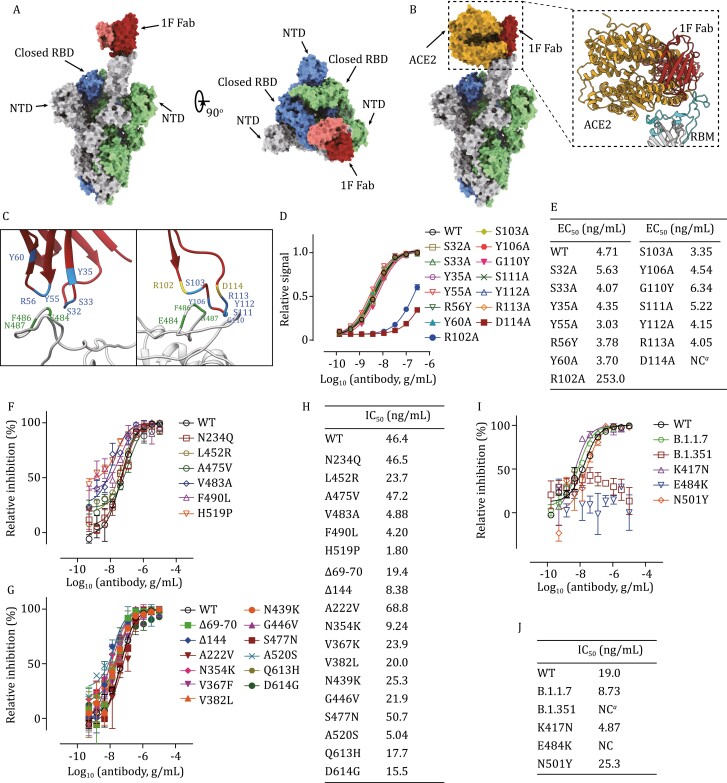
Figure 2.
1F binds to the core epitope and neutralize most of SARS-CoV-2 mutations. (A) Overall structure of 1F Fab in complex with S-trimer. The structure is shown as a molecular surface with a different color for each S monomer as labeled, and the 1F Fab in red and pink (heavy-chain) and (light chain). (B) Clashes between 1F Fab and ACE2 on binding to SARS-CoV-2 S-trimer. ACE2 is shown in yellow. Inset shows close up of the interactions of 1F Fab and ACE2 in the clashed region, showing RBM in cyan. (C) The binding interface between 1F and S-protein, the spatially close residues were colored as indicated. (D) Binding ELISA assays of mutated 1F on RBD. Experiments were performed in triplicate. (E) Summary of EC50 values in ELISA assays performed in (D). NC means EC50 cannot be calculated due to poor binding ability. (F and G) The inhibitory dose curve of 1F on reported immune escape mutants (F) and naturally occurred mutants (G). (H) Summary of IC50 values of 1F in (F) and (G). (I) The inhibitory dose curve of 1F on recently emerged variants and related mutants. (J) Summary of IC50 values of 1F in (I), NC means IC50 cannot be calculated due to poor activity. Experiments were performed in triplicates.