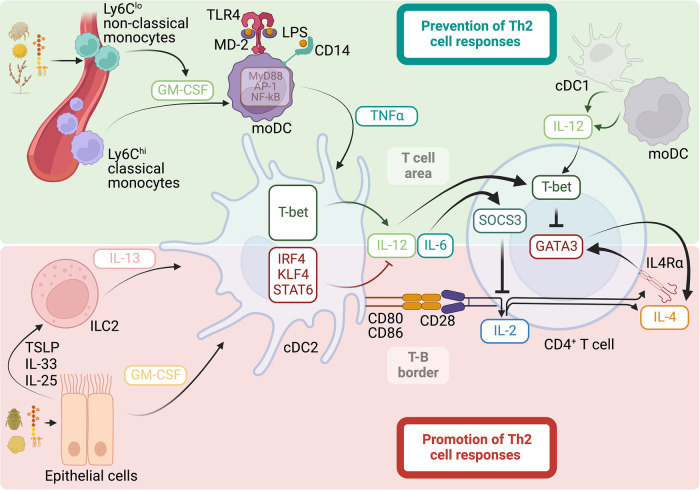
Figure 1.
Mechanisms that promote and prevent Th2 cell responses to allergens. Promotion of Th2 cell responses: allergens with proteolytic activity, cytokines, and microbial products, such as LPS, can activate epithelial cells for subsequent release of the cytokines GM-CSF, TSLP, IL-33, and IL-25. This leads to the activation of ILC2s and the release of IL-13. GM-CSF and IL-13 stimulate the migration and expression of the transcription factors IRF4, KLF4, and STAT6 in cDC2s, ultimately promoting the functional specialization of the cDC2s to support Th2 cell differentiation by reducing the ability of the cDC2s to produce IL-12, while retaining their co-stimulatory ability to foster strong IL-2 responses in CD4+ T cells. Strong and sustained IL-2 signaling in the absence of IL-12 promotes Th2 cell lineage commitment by promoting the expression of IL-4Rα and IL-4, allowing for an IL-4-positive feedback loop that initiates and preserves the Th2 cell phenotype. Prevention of Th2 cell responses: allergens with cysteine protease activity stimulate GM-CSF release from perivascular Ly6Clo non-classical monocytes, guiding the differentiation of Ly6Chi classical monocytes into moDCs. GM-CSF licenses an inflammatory signature in moDCs by increasing the expression of TLR4, CD14, and intracellular signaling members involved in the MyD88/NF-kB/AP-1-dependent pathway. Functional programming of moDCs by GM-CSF allows these cells to increase their sensitivity to LPS and stimulate the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNFα, which guides cDC2 activation for Th2 cell suppression rather than promotion. In particular, TNFα induces the expression of the transcription factor T-bet in cDC2s, which is intrinsically necessary for the ability of cDC2s to produce sustained IL-12 and suppress Th2 cell priming by inducing T-bet and inhibiting GATA3 in CD4+ T cells. cDC2s can also produce IL-6, upregulating SOCS3 in CD4+ T cells and ultimately suppressing IL-2 signaling and early Th2 cell commitment. cDC1s and moDCs are additional sources of IL-12 that contribute to the suppression of Th2 cell responses.