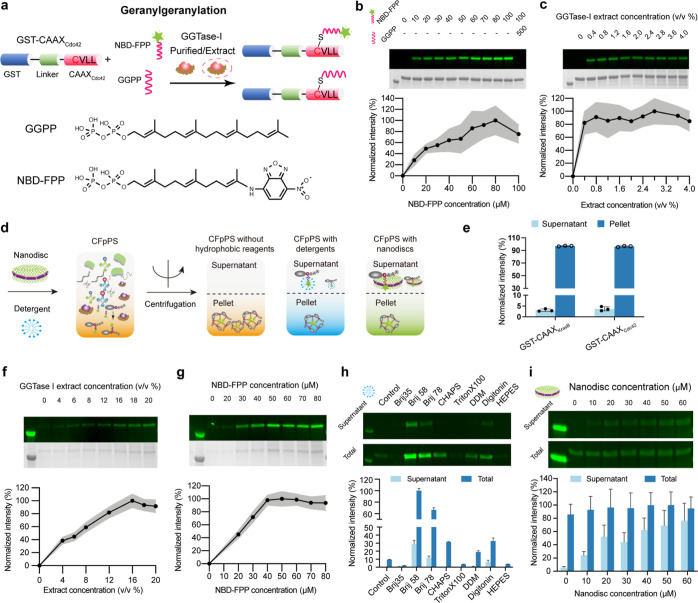
Figure 2.
Establishment of CFpPS for geranylgeranylation. (a) Schematic illustration of the chimeric proteins GST-CAAXCdc42 that are geranylgeranylated via purified GGTase-I- or GGTase-I-enriched extracts. (b) Titration of the NBD-FPP with purified GGTase-I using in-gel fluorescence. The last lane showed the competition assay performed by adding the unlabeled analogue—GGPP—at a concentration fivefold that of the highest tested for the NBD-modified analogue. Concentration (μM) of lipid donor in each reaction is stated above the corresponding gel lane. (c) Titration of GGTase-I-enriched extracts using in-gel fluorescence with10 μM GST-CAAXCdc42 and 80 μM NBD-FPP. Extract concentration is shown as percentage volume of the GGTase-I-enriched extract included in the standard E. coli CFPS. (d) Schematic depicting the expression and solubilization of prenylated CAAX proteins in CFpPS systems with or without solubilizing additives. (e) Prenylated GST-CAAXKrasB or GST-CAAXCdc42 demonstrates low solubility after co-translational prenylation in CFpPS extracts lacking solubilizing additives. 20/80 μM NBD-GPP/FPP were used and prenylated proteins were measured using in-gel fluorescence in the supernatant and the pellet fractions after centrifugation at 20,000g. Measurements were normalized to the mean total protein amount in both the pellet and soluble fractions for each protein. Symbols represent intensity measured in three independent replicates. (f) Concentration optimization of the GGTase-I-enriched extract in the CFpPS system using in-gel fluorescence. Extract concentration is shown as percentage volume of the enriched extract included in the standard E. coli CFPS. (g) In-gel fluorescence analysis for optimizing the concentration of NBD-modified lipid donor in the CFpPS system. (h) Screening of detergents for soluble expression of geranylgeranylated GST-CAAXCdc42. Respective control reactions were performed without any detergent. (i) Nanodisc titration for the soluble expression of GST-CAAXCdc42 in the CFpPS system. Fluorescence intensities of the protein band for each fraction were measured through in-gel fluorescence. Each image (b,c,f,g) includes a representative gel imaged in fluorescence mode to visualize NBD (upper) and colorimetric mode to visualize Coomassie staining (lower). In all graphs, intensity is normalized to the highest average value measured in a dataset. In all graphs (b,c,f,g), mean values from three independent replicates are shown as black dots, while the gray shading represents standard deviation, n = 3.