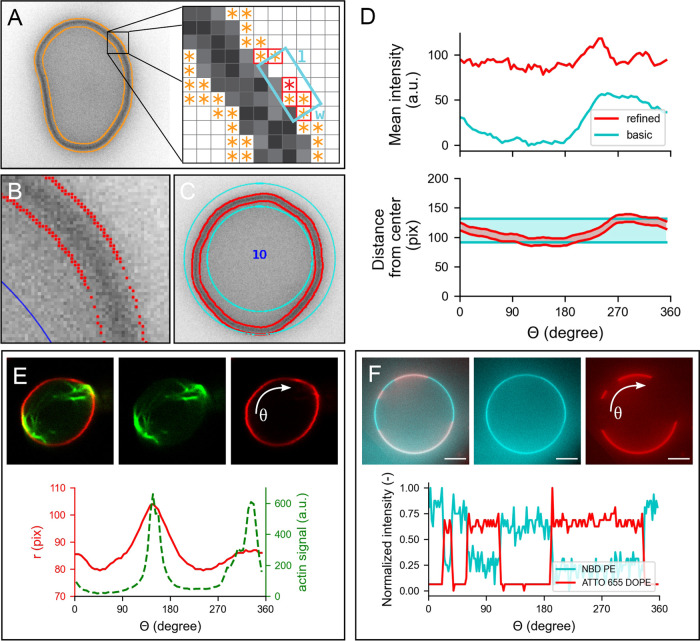
Figure 5.
Membrane analysis by DisGUVery. (A) Schematic overview of the refined detection method. Left: wide-field fluorescence image (inverted) of a GUV with all detected edges (orange). Right: edge points (orange) within the search box (cyan) of size l × w are connected (red border). (B) Zoom-in on membrane edges detected by refined detection (red), displayed on top of the inverted wide-field fluorescence image of a GUV. (C) Segmentation of the membrane area as defined by basic membrane analysis (cyan) and refined membrane detection (red). (D) Angular profile of membrane properties from the vesicle in (C) extracted by basic membrane analysis (blue) and by refined membrane detection (red). Top: mean intensity per angular slice with an angular separation of 5°, and a ring width of 30 pixels for BMA. Bottom: radial distance to inner and outer boundaries from the center of the vesicle. (E) Refined membrane detection on a nonspherical GUV deformed by actin bundles. Insets: composite confocal image of a GUV membrane (red) deformed by actin-fascin bundles (green) (data by F.C. Tsai, from Tsai et al.40). Plot: angular profile of the membrane’s radial distance (red) and integrated actin intensity (green). (F) Basic membrane analysis of a phase-separated membrane containing DOPC:DPPC:cholesterol:NBD-DPPE:ATTO655-DOPE in a 31.8:48:20:0.1:0.1 molar ratio. Insets: image of vesicle labeled with NBD-DPPE (blue) and ATTO655-DOPE (red). Plot: angular profile of both dyes extracted by basic membrane analysis, normalized to unity by subtraction of the minimum signal followed by division by the remaining maximum signal.