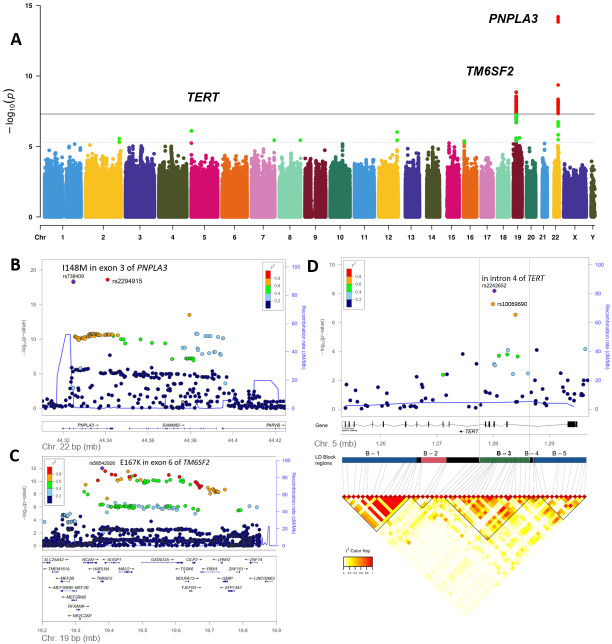
Figure 1.
Genome-wide association study (Discovery GWAS) results. Principal findings of genetic analyses. (A): Manhattan plot of genome-wide association results for alcohol-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the primary discovery cohort. P values (−log10) are shown for SNPs that passed quality control. The genome-wide significance threshold (5×10−8) is shown as a black line. The threshold for replication follow-up (p<5×10−6) is shown as a dashed line. Gene names for replicating loci (table 2) are shown. Variants with significance p<5×10−8 are highlighted in red, those with p<5×10−6 are highlighted in green. (B) Locus plot for HCC risk locus PNPLA3. The −log10 (p values, meta-analysis of discovery and replication samples) are plotted against SNP genomic position based on NCBI Build 37, with the names and location of nearest genes shown at the bottom. The variant with the lowest p value (lead variant) in the discovery analysis in the region is marked by a purple diamond. SNPs are coloured to reflect correlation with the most significant SNP, with red denoting the highest LD (r2 >0.8) with the lead SNP. The top association signal is located in exon 3 of PNPLA3. Estimated recombination rates from the 1000 Genomes Project (hg19, EUR population) are plotted in blue to reflect the local LD structure. (C) Locus plot for HCC risk locus TM6SF2. The top association signal is located in exon 6 of TM6SF2. (D) Locus plot for HCC risk locus TERT. Fine-mapping analysis of the TERT association signals. Annotated LD-Blocks are clusters of strong pairwise LD SNPs and reflect the LD pattern in the Discovery GWAS cohort. The lead association signal is located in intron 4 of the TERT gene (annotated on the reverse strand), located in LD block B-3 spanning from intron 4 to intron 2 of TERT. NCBI, National Center for Biotechnology Information; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.