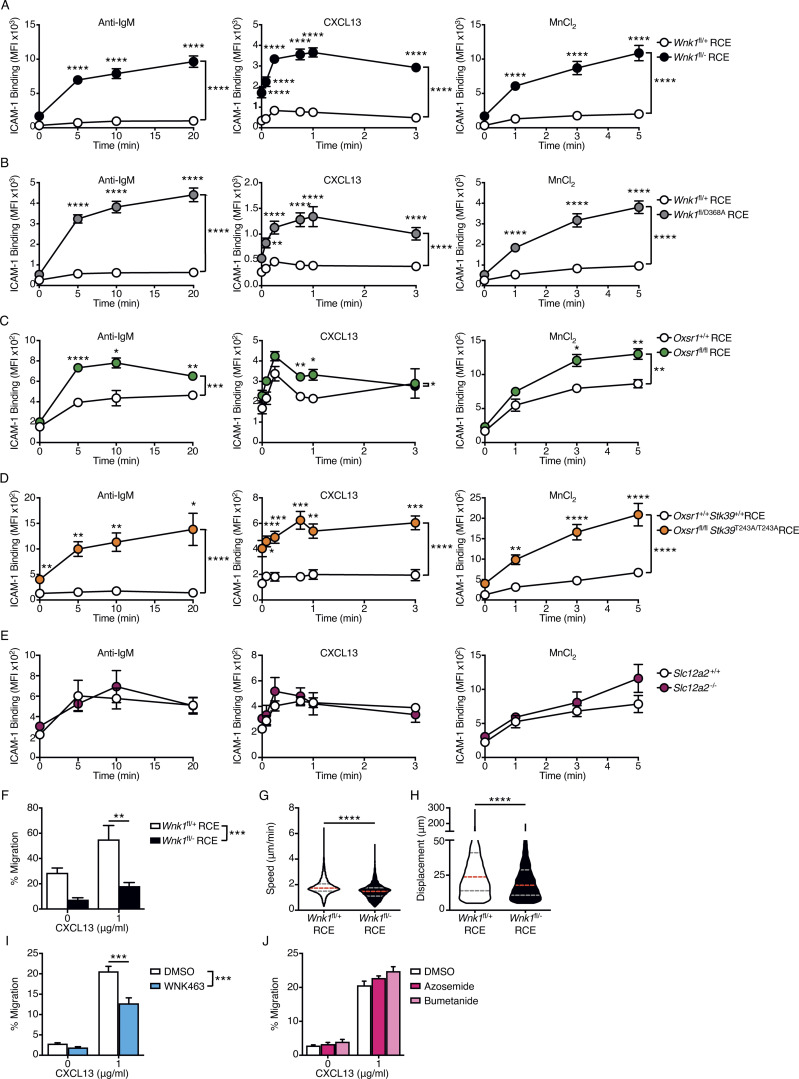
Figure 2.
WNK1 regulates B cell adhesion and migration in vitro. (A–E) Mean ± SEM binding of soluble ICAM-1 complexes to mouse B cells from control B cells and either WNK1-deficient B cells (A), B cells expressing kinase-inactive WNK1-D368A (B), OXSR1-deficient B cells (C), OXSR1-deficient B cells expressing a non-phosphorylatable mutant of STK39-T243A (D), or SLC12A2-deficient B cells (E), stimulated with anti-IgM or CXCL13 or treated with MnCl2 for the indicated times. (F) Mean ± SEM migration of control or WNK1-deficient mouse B cells from the top to the bottom chamber of a Transwell plate in response to CXCL13. (G and H) Violin plots showing mean speed (G) and displacement (H) of control and WNK1-deficient mouse B cells migrating in response to CXCL13. Dashed lines indicate median (red) and 25th and 75th percentiles (gray). (I and J) Mean ± SEM migration of mouse B cells treated with either vehicle (DMSO), an inhibitor of WNK family kinases (WNK463; I), or inhibitors of SLC12A2 (bumetanide and azosemide; J) from the top to the bottom chamber of a Transwell plate in response to CXCL13. Two-way ANOVA (A–F, I, and J), Mann–Whitney test (G and H); *, 0.01 < P < 0.05; **, 0.001 < P < 0.01; ***, 0.0001 < P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Sample sizes: 11 (A); 6 (B); 5 (C); 9 (D); 4 mutant and 6 control (E); 4 mutant and 5 control (F); 5,245 mutant cells and 7,289 control cells (G and H); and 4 (I and J). Data are pooled from two independent experiments.