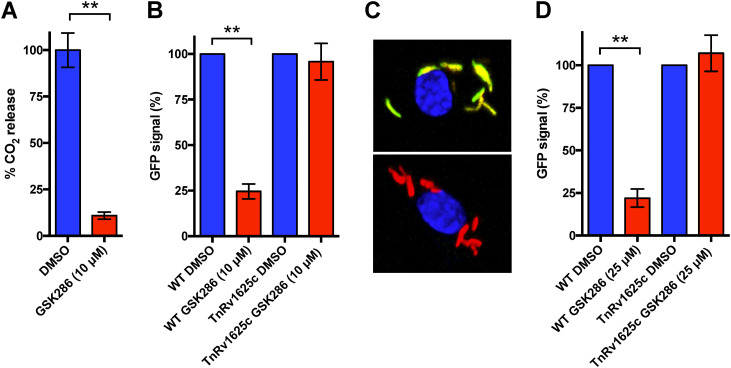
FIG 2.
GSK286 treatment reduces cholesterol-derived propionyl-CoA pools in M. tuberculosis. (A) GSK286 blocks the degradative release of 14CO2 from 14C-cholesterol in wild-type M. tuberculosis during growth in cholesterol-acetate media. (B) The GFP signal from the prpD′::GFP reporter decreases in wild-type M. tuberculosis in an Rv1625c-dependent manner following treatment with GSK286 during growth in cholesterol-acetate media. (C) Representative images of macrophages infected with wild-type M. tuberculosis carrying the prpD′::GFP reporter (green), the constitutive M. tuberculosis mCherry signal (red), and DAPI stain (blue). DMSO-treated (top panel) and GSK286-treated (bottom panel) samples are shown. (D) Flow cytometric quantification of the prpD′::GFP reporter signal M. tuberculosis isolated from infected macrophages. The median GFP signal was quantified from 10,000 bacteria and calculated relative to the DMSO control for each strain of bacteria. Bars represent means ± the standard deviations (SD; n = 4) from two independent replicates with two technical replicates each. (A) **, P < 0.05 (Student t test); (B and D) **, P < 0.05 (ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test).