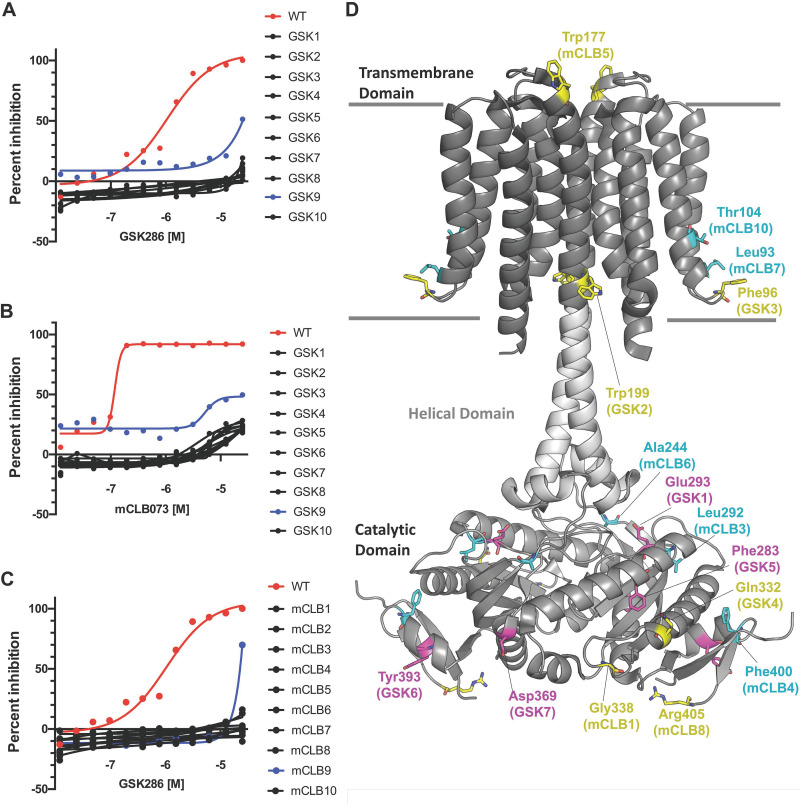
FIG 4.
Spontaneous resistance mutations confer cross-resistance to the Rv1625c agonists. (A) GSK286 MIC assay in cholesterol media with resistant mutants raised against GSK286 on cholesterol. (B) mCLB073 MIC assay in cholesterol media with resistant mutants raised against GSK286 on cholesterol. (C) GSK286 MIC assay in cholesterol media with resistant mutants raised against mCLB073 on cholesterol. The data are from one experiment with two technical replicates (n = 2). Symbols indicate means, and curves display the nonlinear fit of dose response. Inhibition was calculated using alamarBlue fluorescence with 100% inhibition established using rifampicin treatment (10 μM); all inhibition values are normalized to this value. The x-axis values are logarithms of concentrations expressed as a molar unit. (D) Mutations mapped onto the structure of Rv1625c. The overall fold (PDB ID 7YZK) is shown as a cartoon representation with the transmembrane, helical, and catalytic domains shown as different shades of gray with the approximate boundaries of the membrane drawn as gray lines. The location of missense mutations arising from GSK286 treatment in this study (Table 1) are highlighted as magenta sticks. The locations of cross-resistant missense mutations arising from mCLB073 treatment are shown as cyan sticks. The location of all other mutations, including nonsense, insertion, and frameshift mutations conferring resistance to GSK286, are highlighted as yellow sticks.