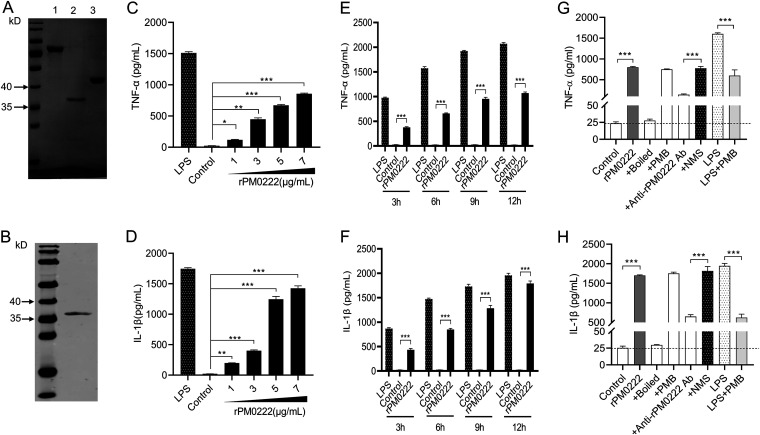
FIG 1.
rPM0222-induced secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by murine peritoneal exudate macrophages. (A) Lane 1, purification of recombinant MBP-PM0222 fusion protein. Lane 2, purification of rPM0222 protein. Lane 3, purification of MBP. (B) rPM0222 reacted with the anti-His antibody. (C and D) The murine peritoneal exudate macrophages were incubated with 5 μg/mL rPM0222 (1, 3, 5, or 7 μg/mL) for 6 h. The TNF-α and IL-1β levels in cell culture supernatants were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (E and F) The murine peritoneal exudate macrophages were incubated with 5 μg/mL rPM0222, and the TNF-α and IL-1β levels in cell culture supernatants were measured using ELISA at 3, 6, 9, or 12 h. (G and H) The murine peritoneal exudate macrophages were incubated with 5 μg/mL rPM0222 for 6 h, and the TNF-α and IL-1β levels in cell culture supernatants were measured using ELISA. rPM0222 was pretreated with polymyxin B (+PMB) and boiled (+boiled) at 100°C for 10 min to confirm that the activation of murine peritoneal exudate macrophages was because of rPM0222 and not lipopolysaccharide (LPS). LPS (1 μg/mL) was used as a positive control and pretreated with polymyxin B (PMB) to confirm the action of PMB (LPS+PMB). To confirm that rPM0222 specifically promotes the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, the proteins (5 μg/mL) were pretreated with the anti-rPM0222 serum (+anti-rPM0222 Ab, 1:500) or control mouse serum (+NMS, 1:500). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. The experiments were performed at least three times.