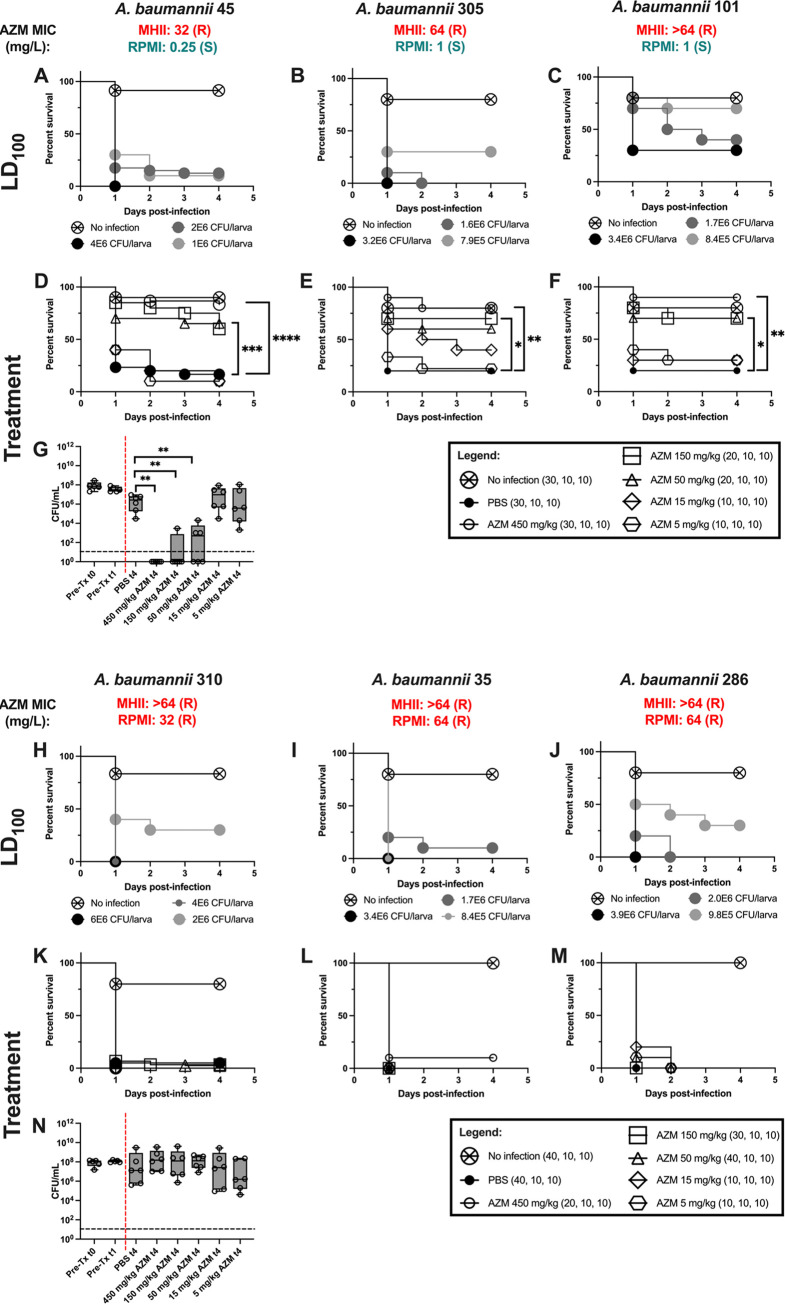
FIG 2.
In vivo AZM efficacy. (A to C, H to J) Galleria mellonella larvae were challenged with various bacterial inocula to determine strain-specific LD100 values. (D to F, K to M) To determine AZM efficacy, Galleria mellonella larvae were infected with lethal inoculum using A. baumannii strains 45 (1.90E6 to 2.08E6 CFU/larva), 305 (3.33E6 CFU/larva), 101 (3.90E6 CFU/larva), 310 (4.05E6 to 6.15E6 CFU/larva), 35 (2.95E6 CFU/larva), or 286 (2.20E6 CFU/larva) before being treated with PBS or AZM. No infection control received 2 doses of PBS. Statistical comparisons were made using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test to compare survival between PBS-treated and each AZM-treated group; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001. N values in parentheses are in order of A. baumannii strains 45, 305, and 101 (top) or A. baumannii strains 310, 35, and 286 (bottom) and are nonuniform across groups because multiple experiments testing different dosages are represented in the figure. (G, N) Survival experiments were performed as described, and hemolymph was collected and plated at 0 h postinfection (PI) before treatment (t0), 1 h PI before treatment (t1), and 4 h PI after treatment (t4). Tx, treatment. Statistical comparisons were made using the Mann-Whitney test to compare the CFU burden between the PBS-treated group and each AZM-treated group at 4 h PI. The CFU limit of detection (1E1 CFU/mL) is delineated by a horizontal black line. Pretreatment and posttreatment groups are separated by a vertical red line (n = 5 for each pretreatment group; n = 6 for each posttreatment group).