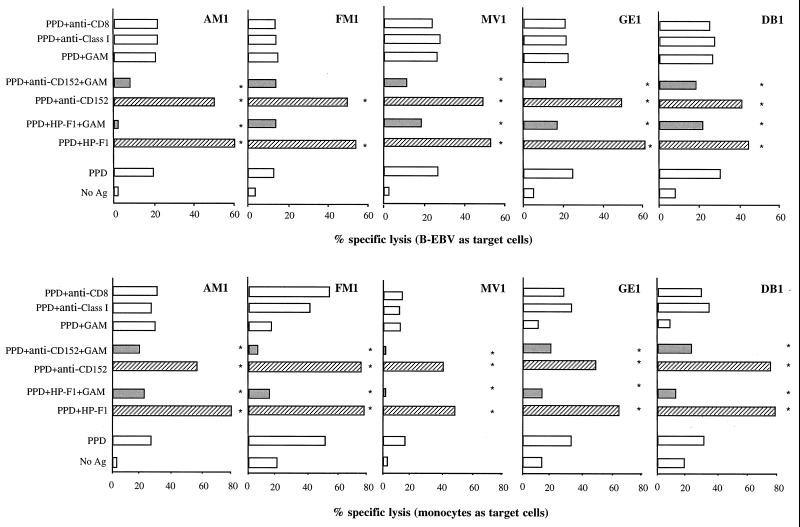
FIG. 5.
CD85/LIR-1/ILT2 and CD152 regulate the antigen-specific cytotoxic activity of CD4+ T-cell clones. The function of cytolytic CD4+ T-cell clones against autologous antigen-presenting B-EBV cells or monocytes was assayed in a conventional 4-h 51Cr-release assay, carried out in the absence or presence of soluble MAbs, alone or cross-linked by GAM antiserum. Soluble HP-F1 or anti-CD152 MAb significantly increased specific lysis, while the same MAb cross-linked by GAM antiserum reduced lysis. Control samples were treated with GAM antiserum alone or two irrelevant MAbs (i.e., anti-CD8 or anti-MHC class I MAb). Asterisks indicate values that are significantly different for PPD, PPD plus HP-F1, PPD plus HP-F1 plus GAM, PPD plus anti-CD152, and PPD plus anti-CD152 plus GAM culture conditions. P < 0.05. ▨, blocking MAb conditions; ░⃞, cross-linking of MAb specific for inhibitory receptors.