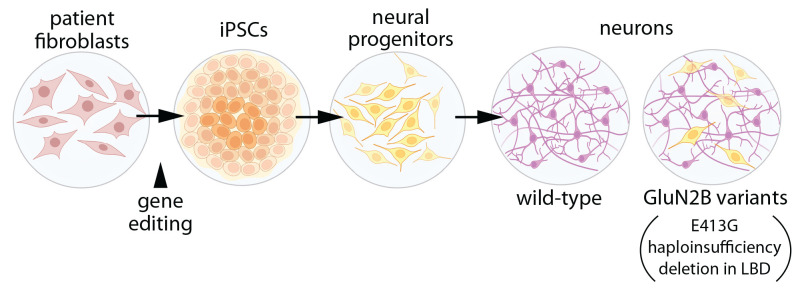
Figure 2.
Expression of GluN2B variants interferes with neuronal differentiation. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were generated with either: (1) GluN2B harboring the disease-associated missense mutation, E413G, within the ligand-binding domain (LBD); (2) deletion of a section of the GluN2B LBD, or (3) GluN2B haploinsufficiency (Bell et al., 2018). Neural progenitor cells were generated from iPSCs, then differentiated into forebrain neurons. In differentiated cells with GluN2B variants, expression of genes related to cell proliferation and pluripotency was elevated, while genes associated with neuronal differentiation were reduced, when compared to cells with two alleles of wild-type GluN2B. Illustrations were partially created with BioRender.com.