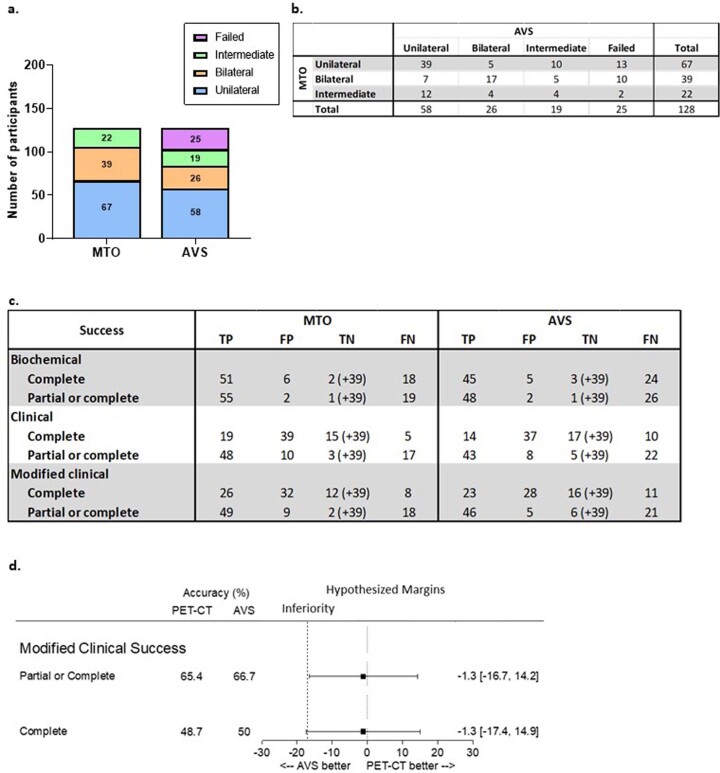
Extended Data Fig. 1. Results from MTO and AVS.
a. Number of patients in whom MTO or AVS identified unilateral or bilateral primary aldosteronism (PA). ‘Intermediate’ suggests some asymmetry in the adrenals but not meeting criteria for unilateral disease. ‘Failed’ indicates unsuccessful cannulation of adrenal vein(s) and therefore inability to interpret AVS result. n = 128, all patients who reached the primary endpoint time-point (6 or 9-12 months post surgery or medical therapy respectively). b. Cross tabulation table showing results from MTO and AVS, indicating relative contribution of each investigation. n = 128. c. Accuracy of each investigation in predicting biochemical and clinical outcomes post surgery. The table assumes the 39 patients found to have bilateral disease on both investigations and did not go for surgery, indicated by brackets, were true negatives. This assumption (both investigations were accurate) allows calculation of the false positive rates but does not differentiate between the relative performance of each investigation, which is determined by cases where the investigation outcomes disagreed. *n = 116 for biochemical success, n = 117 for clinical success, based on a total of 78 patients who went underwent adrenalectomy and 39 who were thought to have bilateral disease based on both investigations. TP, true positive; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; FN, false negative. d. Modified clinical success outcomes. Forest plot of modified clinical success outcomes, determined by change in number of classes of antihypertensive medications (for definitions please refer to Supplementary Table 3). Column 2 and 3 show percentage of success accurately predicted by MTO and AVS respectively. Right hand column show percentage difference. The centre for the error bars is the Estimated Difference in Accuracy in (%). It, along with the 95% CI (shown in square brackets), is given in the figure’s last 3 columns. Non-inferiority p values: partial or complete modified clinical success p = 0.045; complete modified clinical success p = 0.057. The BinomDiffCI() function from R was used to calculate the 95% CI61 and to estimate the p-values using a 2-sided test. n = 78.