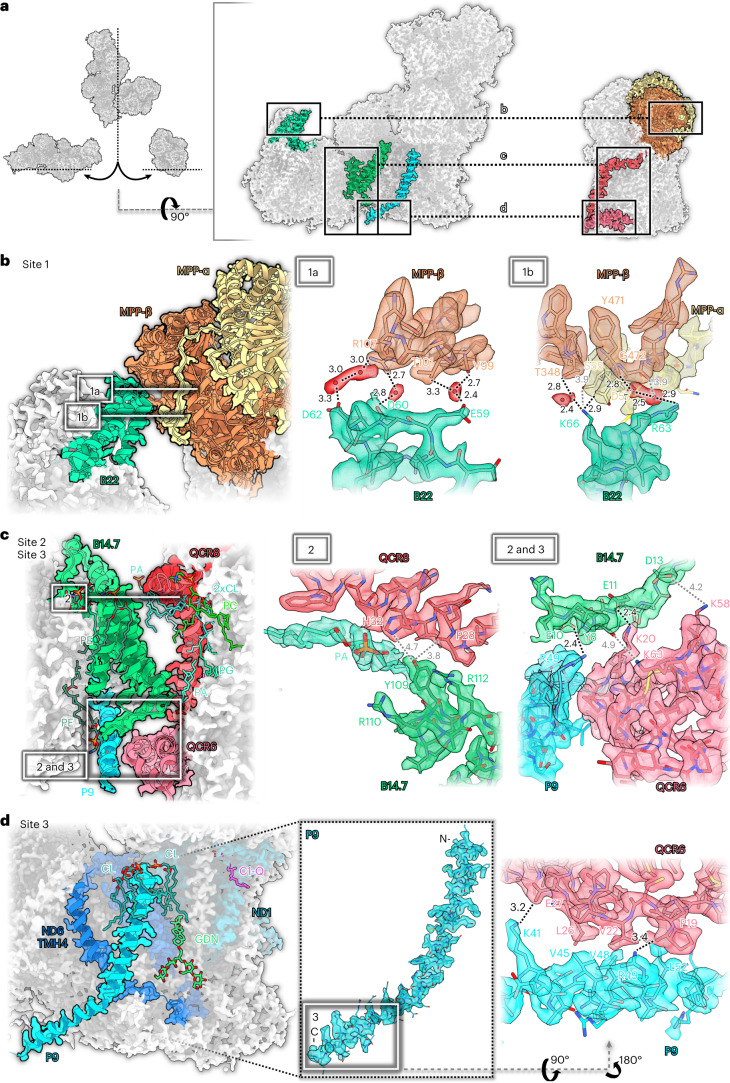
Fig. 4. Three interaction sites of complexes I and III2 in the Arabidopsis supercomplex.
a, Overview. b, Interaction site 1: B22 (green) of complex I binds to MPP-β (orange) and MPP-α (yellow) of complex III2. 1a and 1b show two roughly orthogonal views of interaction site 1. Interaction is mediated by hydrogen bonds including water molecules (red) and salt bridges. c, In site 2, B14.7 of complex I binds to QCR8 (red) and QCR6 (pink) of complex III2. In addition to polar contacts, the interaction is mediated by a set of membrane phospholipids. In site 3, binding to QCR6 involves the newly identified subunit P9 (light blue) of complex I. d, Also in site 3, the C-terminal part of P9 binds to QCR6 of complex III2 by salt bridges and hydrophobic contacts. Interacting amino acid residues are indicated by the one-letter code. Lipids: CL, cardiolipin; GDN, synthetic digitonin analogue glyco-diosgenin; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PG, phosphatidyl-glycerol; Q, ubiquinone/ubiquinol. The network of hydrogen bonds (in Å) is indicated by black (<3.5 Å) or grey (>3.5 Å) dotted lines.