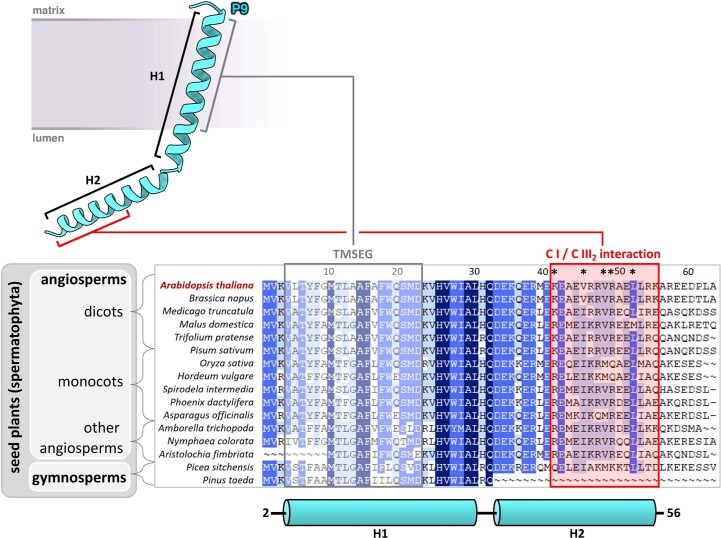
Extended Data Fig. 1. Phylogenetic analysis of complex I subunit P9.
P9 is a two-helix (H1, H2) peptide that spans the inner mitochondrial membrane from the matrix to the lumenal side by its transmembrane segment (TMSEG). For phylogenetic analysis, Arabidopsis P9 (At1g67785) was used to search the non-redundant protein sequences (nr) database at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, “https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/”) using standard settings. >100 homologous sequences were identified below an E-value of 1e-4. All sequences were from seed plants (spermatophyta). Sixteen sequences were selected for building a multiple sequence alignment using Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/); five sequences for dicots and monocots, respectively, and all identified sequences of other spermatophyta clades. Amino acid positions conserved in 16/16 sequences are highlighted in dark blue, amino acid positions conserved in ≥14/16 sequences in mid-blue and amino acid positions conserved in ≥10/16 sequences in light blue. Phylogenetic clades are indicated to the left of the alignment. The topology model of P9 is indicated above the alignment. The model was built into the cryo-EM density of the Arabidopsis I + III2 supercomplex from valine at position 2 to alanine at position 56. The positions of its two alpha-helices are shown below the alignment. The complex III2 interacting segment is shown in red. Residues K41, V45, V48, R49, L52 of Arabidopsis P9 that interact directly with complex III2 are indicated by asterisks (see Fig. 4c and d). Accession of sequences. Arabidopsis thaliana: At1g67785, Brassica napus: CAF2186799, Medicago truncatula: XP_013446710, Malus domestica: XP_028959763, Trifolium pratense: XP_045824609, Pisum sativum: XP_050898094, Oryza sativa: NP_001392381, Hordeum vulgare: XP_044978029, Spirodela intermedia: CAA2619857, Phoenix dactylifera: XP_008797106, Asparagus officinalis: XP_020253321, Amborella trichopoda: XP_020527559, Nymphaea colorata: XP_031475842, Aristolochia fimbriata: KAG9445531, Picea sitchensis: ABK24944, Pinus taeda: AFG45619.