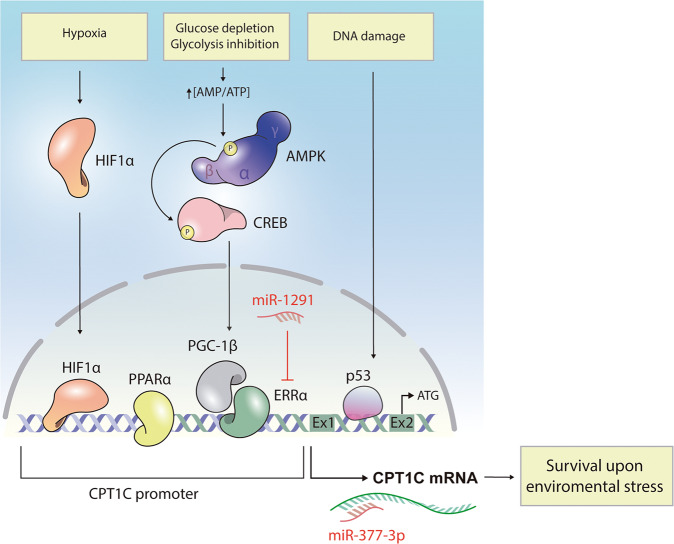
Fig. 2. Regulation of CPT1C expression.
Metabolic challenges such as hypoxia and nutrient deprivation increase CPT1C expression in most cancer cells, promoting metabolic adaptation and survival in response to these environmental stressors. On the one hand, low oxygen levels promote accumulation of the HIF1α transcription factor, which is translocated to the nucleus to bind the Cpt1c promoter and activate gene transcription. On the other hand, glucose depletion and glycolysis inhibition increase the AMP/ATP ratio leading to activation of AMPK, which in turn, phosphorylates and activates the CREB transcription factor. Phosphorylated CREB increases expression of the PGC-1β and ERRα transcription factors, ultimately promoting Cpt1c transcription. PPARα activates CPT1C expression by binding directly to the promoter region. p53 is activated by DNA-damaging stimuli and binds to the first intron of the Cpt1c, thereby enhancing CPT1C expression. Interestingly, 2 different miRNAs have been described that downregulate this signaling pathway, one acting on ERRα expression, and the other on CPT1C expression.