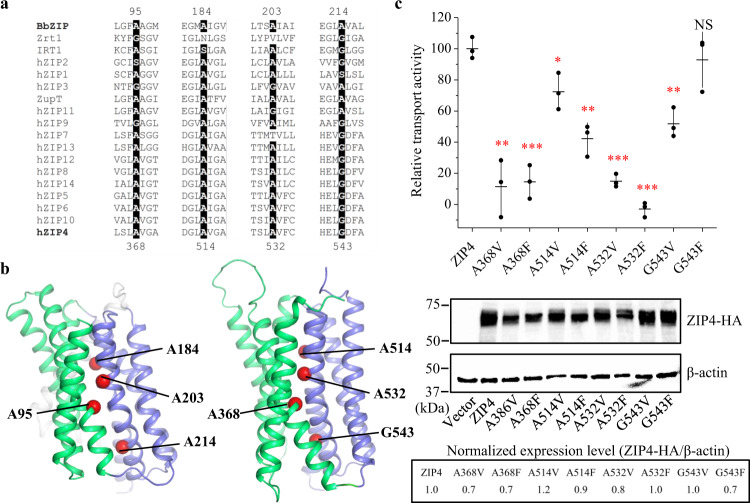
Fig. 9. Functional characterization of the conserved small residues at the domain interface.
a Multiple sequence alignment of representative ZIPs from major subfamilies. Conserved small residues (Ala, Gly, or Ser) identified at the interface between the transport domain and the scaffold domain are highlighted. b Mapping of the conserved small residues in BbZIP and in human ZIP4. The Cα atoms of the residues chosen for mutagenesis are depicted as red spheres. Only the structure of ZIP4 transmembrane domain (predicted by AlphaFold, https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q6P5W5) is shown. c Zinc transport activities of ZIP4 and the variants. HEK293T cells transiently transfected with ZIP4 or the variants were applied to the radioactive 65Zn transport assay. The relative transport activity of each variant was calibrated with the normalized expression level, which was estimated in Western blot experiments, and expressed as the percentage of the activity of the wild type ZIP4. The shown data are from one representative experiment and 2-3 independent experiments with similar results were conducted for each variant. Three biological replicates were included for each variant in one experiment. The horizontal bar of the scatter dot plot represents the mean and the vertical bar indicates the standard deviation. The asterisks indicate the significant differences between the variants and the wild type ZIP4 (two-sided Student’s t tests: *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; NS—no significant difference). The exact P values are 0.0015, 0.00032, 0.024, 0.0012, 0.000053, 0.000028, 0.002, and 0.56 for the variants of A368V, A368F, A514V, A514F, A532V, A532F, G543V, and G543F, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.