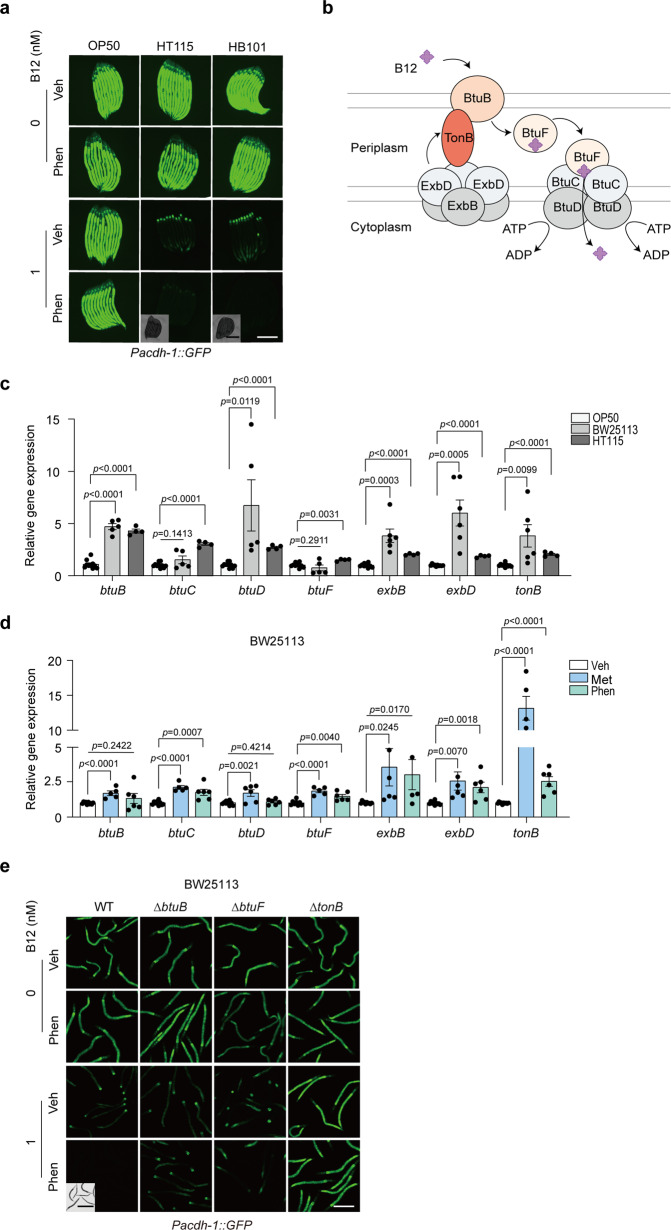
Fig. 2. The B12 transport machinery plays essential roles in phenformin-mediated bacterial B12 accumulation.
a Representative images of Pacdh-1::GFP worms fed bacterial strains OP50, HT115, and HB101 pretreated with B12 and/or 4 mM phenformin. N = 3 independent experiments containing at least 30 worms per group. b Diagram of the B12 transport machinery in E. coli. c–d Relative mRNA levels of genes involved in B12 transport in OP50, BW25113, and HT115 bacteria (c) and BW25113 with 200 mM metformin/4 mM phenformin treatment or not (d). For (c, d), N = 2 independent experiments containing 4–6 replicates. The statistical significance values were determined by multiple t tests. Error bars denoted the S.E.M. e Representative images of Pacdh-1::GFP worms fed WT and B12 transporter mutant strains pretreated with B12 and/or 4 mM phenformin. WT, BW25113. N = 3 independent experiments containing at least 30 worms per group. Scale bar: 250 μm (fluorescence images) and 500 μm (bright field images) for (a) and (e).