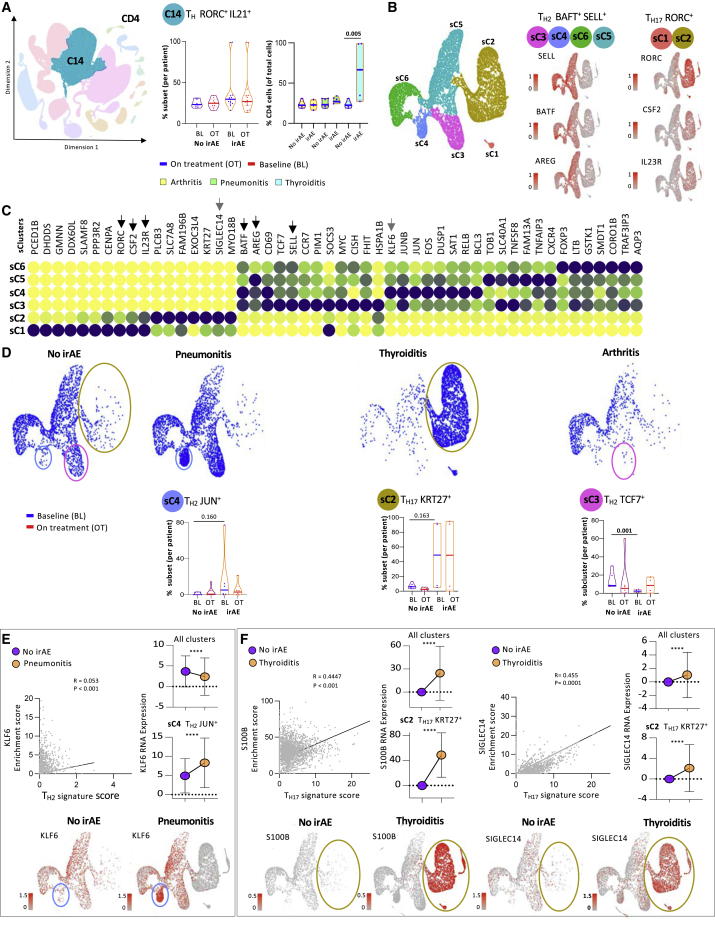
Figure 4.
Selected subsets of CD4 helper T cells are associated with organ-specific irAEs
(A) Representative KNetL plot of cluster 14 and mean percentage differences in TH RORC+ IL21+ cells per patient and across the disease groups: arthritis, pneumonitis, and thyroiditis.
(B) Subclustering of C14 cells into 6 sub clusters: sC1–sC6. Representative genes are shown separately.
(C) Heatmap showing the expression of markers associated with different subclusters among TH2 and TH17 families of cells. Black arrows indicate the subset defining markers.
(D) Differential clustering among the clinical irAE groups at baseline. Quantification of the percentages of cells in three clusters (sC3, sC4, and sC2) among irAE and no-irAE groups. The patients elected for each of the no-irAE groups were selected to match the type of underlying tumor.
(E) Correlation and RNA expression plots highlighting the association of candidate gene markers with TH2 and TH1723 clusters based on enrichment score. Representative KNetL plots showing the expression of candidate gene markers KLF6, S100B, and SIGLEC14 specifying the predictive cell populations present in pneumonitis and thyroiditis.
Statistical significance for unpaired comparisons was performed by Student’s t test applying Mann-Whitney test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. p value, exact, two-tailed, the center lines denote the mean of SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.