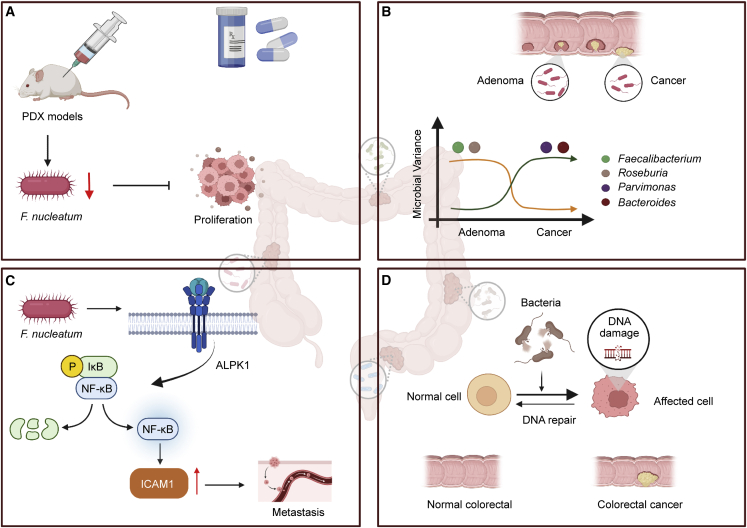
Figure 4.
Characterization of the intratumoral microbiota in colorectal cancer (CRC)
(A) Treatment of Fusobacterium-containing PDX models with metronidazole inhibited tumor growth.
(B) Changes in individual microbial abundance within tumors vary along the adenoma-cancer sequence. The abundance of intratumoral variants of Bacteroides and Parvimonas increases from adenoma to carcinoma. The abundance of intratumoral variants of Faecalibacterium and Roseburia decreases from adenoma to carcinoma.
(C) F. nucleatum induced ALPK1 to activate the NF-κB pathway, leading to the upregulation of ICAM1.
(D) The development of CRC could be caused in part by DNA damage caused by substances released by bacterial infection.