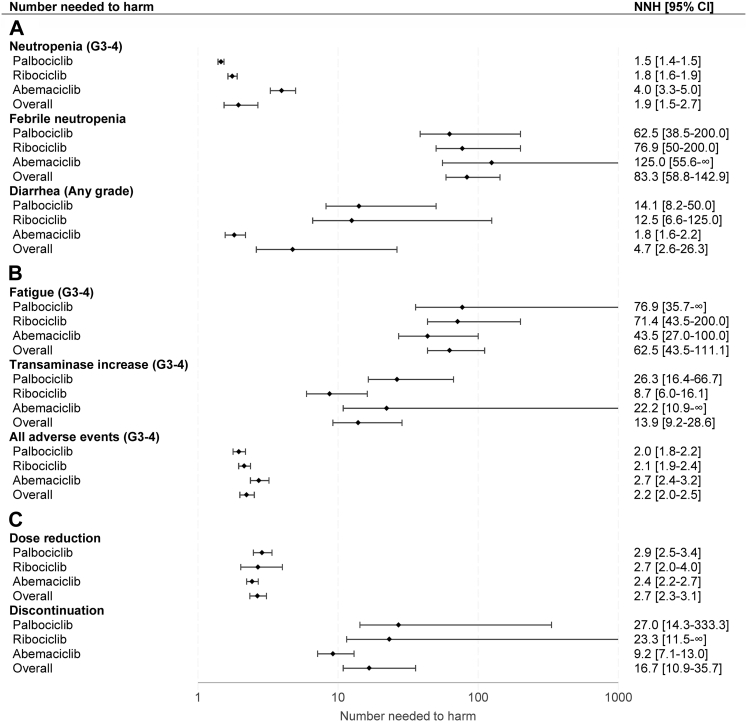
Fig. 3.
Number needed to harm for common adverse events. Values are displayed on a logarithmic scale. Results from the random-effects model were used to compute NNHs. Higher NNH correlates to less toxicity. When the lower limit of the risk difference crosses 0, the confidence interval for the NNH encompasses two region values, a positive to +∞ and a negative to ∞. By convention, only positive values are reported. NNH = number needed to harm. 95% CI = 95% confidence interval. G = grade.