Figure 4.
Co-localization of BRPF1, H3K4me3, and H3K23ac on fundamental and stemness genes in human ESCs
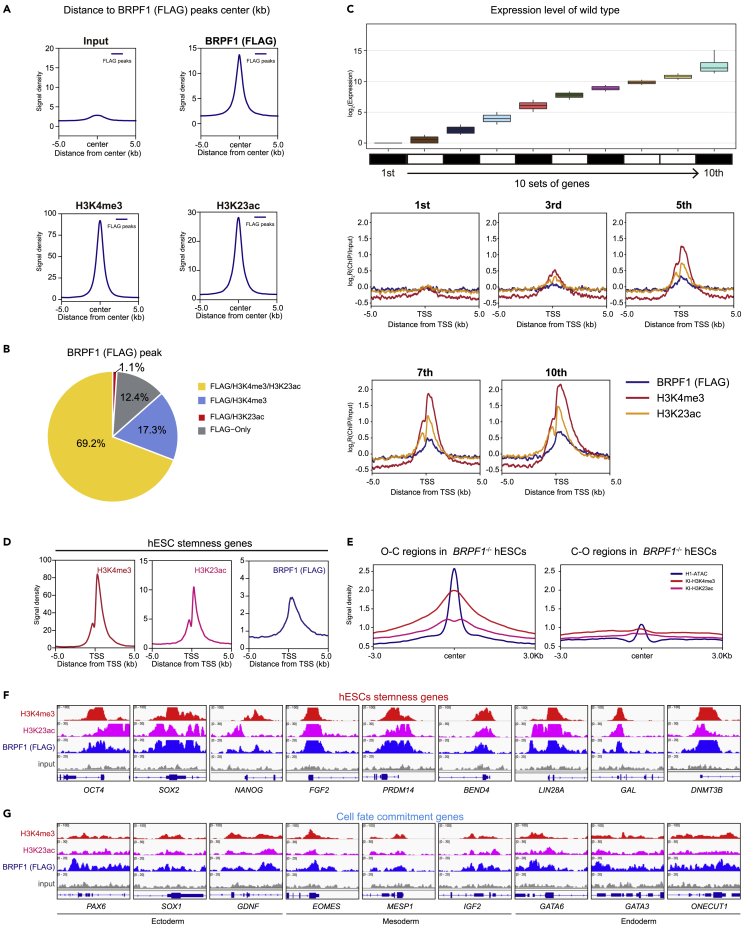
(A) Signal densities for input, H3K4me3, BRPF1 (FLAG), and H3K23ac ChIP-seq data around ±5 kb centered on BRPF1 (FLAG) associated peaks in KI hESCs.
(B) BRPF1 (FLAG) associated peaks classification, H3K4me3/H3K23ac/FLAG co-localization peaks (yellow); H3K4me3/FLAG co-localization peaks (indigo); H3K23ac/FLAG co-localization peaks (red); and only FLAG localization peaks (none, gray).
(C) Upper panel, all genes from the H1 RNA-sep in Figure 1 broken down by decile of expression (1st being lowest 10% and 10th being highest 10%). lower panel, The average signal intensity of H3K4me3, BRPF1 (FLAG), and H3K23ac ± 5 kb around the TSS of 1st, 3st, 5st, 7st, and 10st.
(D) Signal densities for H3K4me3, BRPF1 (FLAG), and H3K23ac ChIP-seq data ±5 kb around the TSS of selected stemness genes in KI hESCs.
(E) Signal densities of H3K4me3, H3K23ac, and ATAC-seq data ±3 kb around the peak center of open to close (O-C) and close to open (C-O) in WT hESCs.
(F and G) Genomic views of signal densities of ChIP-seq data of H3K4me3 (red), BRPF1 (FLAG) (blue), and H3K23ac (purple) on selected genes in KI hESCs. These selected genes include (F) hESCs stemness genes and (G) cell fate commitment genes.