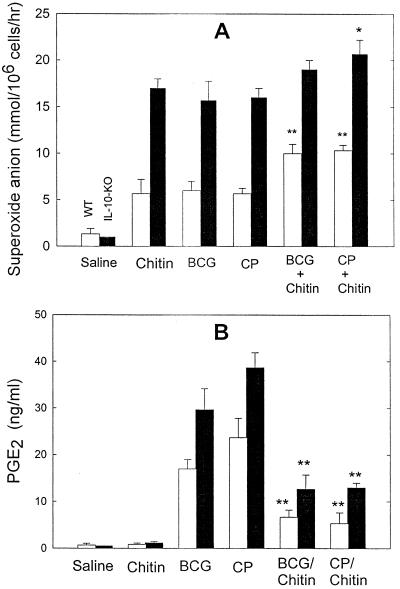
FIG. 1.
Alveolar Mφ priming and the formation of PGE2-Mφ in the spleen following HK BCG administration. WT and IL-10-KO mice intravenously received 0.5 mg of HK BCG, chitin, or HK C. parvum (CP; positive control). Mice that received 0.2 ml of saline served as negative controls. Furthermore, some groups received chitin (0.5 mg) mixed with HK BCG (0.5 mg) or HK C. parvum (0.5 mg). (A) Superoxide anion release by alveolar Mφ. On day 3, alveolar Mφ were assayed in vitro for superoxide anion release by phorbol myristate acetate (1 μM). Superoxide anion levels were measured by a cytochrome c reduction assay as described in Materials and Methods. Data are means plus standard deviation; n = 4. ∗, P < 0.05 compared with chitin alone; ∗∗, P < 0.01 compared with BCG alone or C. parvum alone. (B) PGE2 release by spleen Mφ. On day 7, splenic Mφ were isolated from the other set of experimental groups. Mφ in each group were pooled and incubated in serum-free RPMI 1640 medium containing A23187 at 10−6 M for 2 h. The levels of PGE2 were measured by ELISA. Values are means plus standard deviations; n = 3. ∗∗, P < 0.01 compared with BCG alone or C. parvum alone.