Fig. 15.
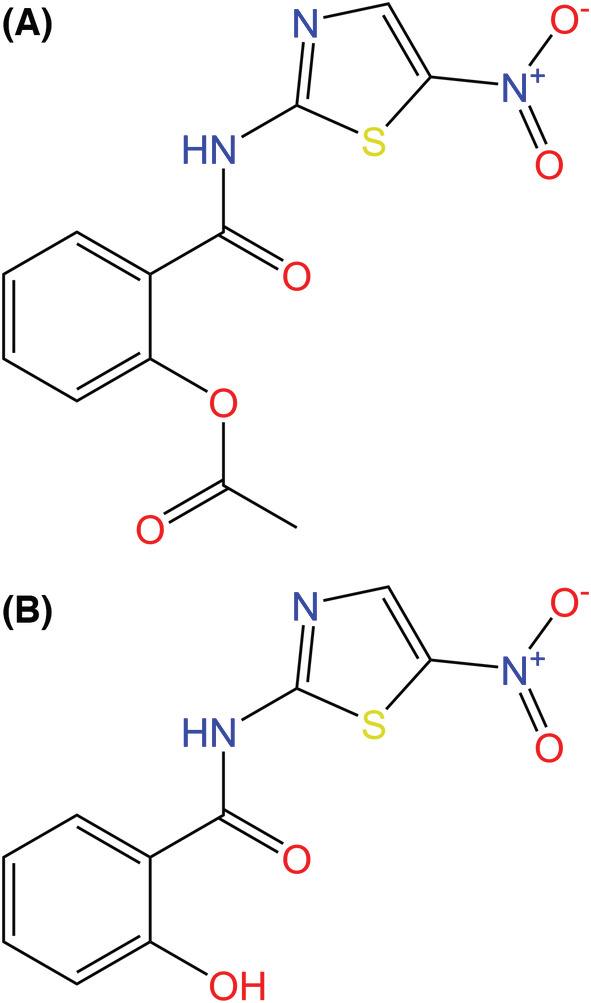
(A) Chemical structures of nitazoxanide (NTZ) and (B) tizoxanide (TIZ), the active metabolite of NTZ, which is formed through rapid hydrolysis of NTZ's acetyl group by plasma esterases. NTZ and its derivatives have been found to have antimicrobial, antiparasitic, and antiviral properties. NTZ is theorized to have antiviral activity against SARS‐CoV‐2 by inhibiting viral entry and/or post‐translational processing [161, 168].
