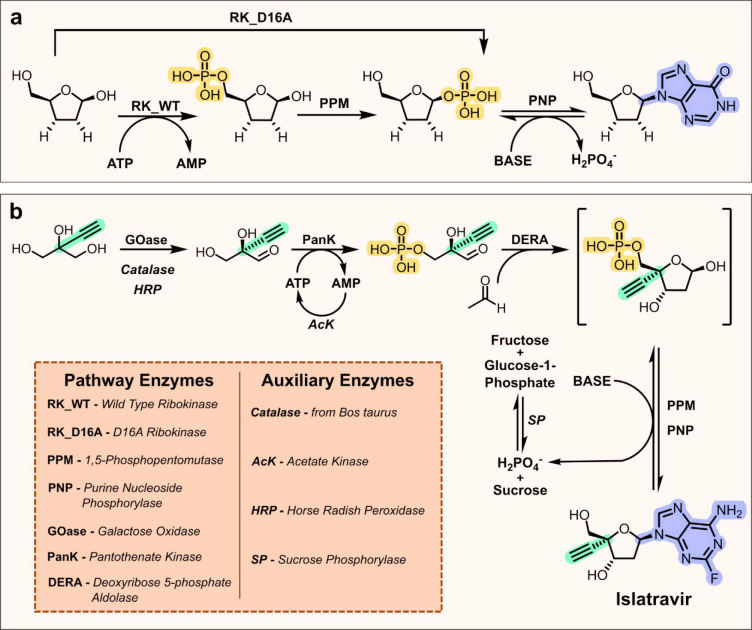
Figure 2.
Biocatalytic approaches to nucleoside analogues. (a) Enzyme cascade for the synthesis of didanosine involving a ribokinase (RK), phosphopentomutase (PPM), and purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP). The RK variant D16A has mechanistic promiscuity and can catalyze direct 1′-ribose phosphorylation, avoiding the requirement for PPMs. (b) Enzyme cascade for the synthesis of Islatravir. The first step involves a galactose oxidase (GOase) catalyzed desymmetrization using auxiliary enzymes catalase and HRP. In the second step, pantothenate kinase (PanK) catalyzes substrate phosphorylation using ATP, which is recycled by acetate kinase (AcK) and acetylphosphate. The final step involves deoxyribose 5-phosphate aldolase (DERA), PPM and PNP, and a sucrose phosphorylase (SP) auxiliary enzyme to drive the equilibrium.