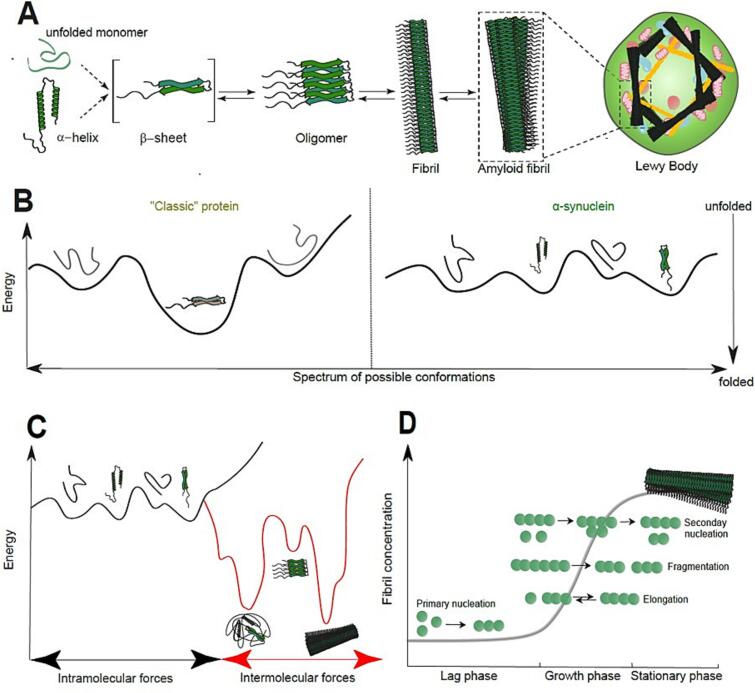
Fig. 1.
α-syn aggregation (adapted from (Bezard and Dehay, 2022). A) Schematic summary of the aggregation pathway of α-syn. Different monomeric species exist in a continuous equilibrium. Aggregation of α-syn usually involves the formation of rich b-sheet-like assemblies, which precede the formation of more complex fibrillated forms of the protein found in Lewy Bodies. B) Energy diagram illustrating protein structural transition. Unlike classic proteins, where different conformational forms are associated with relatively deep energy pits (left), α-syn structure oscillates continuously between various conformations with similar energy levels (right). C) Under special conditions, α-syn can adopt extremely stable forms, termed amyloid structure, which is then very hard to reverse. D) α-syn aggregation process is a highly complex process. Nonetheless, it is generally accepted that amyloid fibril formation is a process that relies on several stages: primary nucleation, growth, and proliferation by elongation and secondary nucleation. These phases are commonly subdivided into three depending on fibril mass: elongation, growth, and stationary.