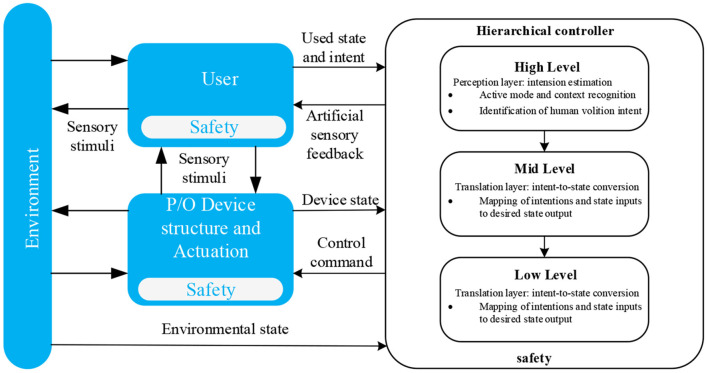
Figure 7.
Generalized control framework for lower limbs. Three stages are essential for LLEC: high-level, mid-level, and low-level. First, the layer accomplishes action mode recognition on the high-level stage, enabling the controller to switch between mid-level controllers suitable for various locomotive duties, such as level walking, stair ascent, standing, hopping, and so on. Second, at the mid-level stage, a layer converts human intentions into instructions or estimate points that are then transferred to local controllers, each placed at every linkage of the exoskeleton. Finally, in the low-level stage, the layer accomplishes real-time control in each joint by performing feed-forward and feed-backward control loops (Tucker et al., 2015).