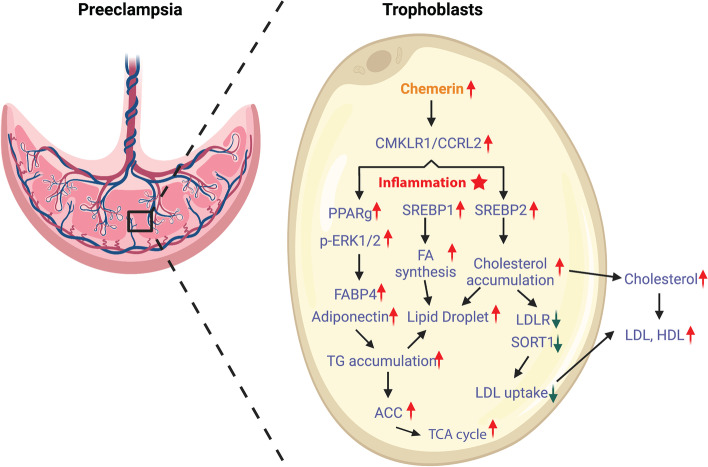
Fig. 6.
Schematic view of roles of chemerin in preeclampsia dyslipidemia. In preeclampsia condition, a high level of chemerin is released from trophoblasts in the placenta, inducing an inflammatory condition and further increasing the levels of placental lipids (TG, Chol, and phospholipids), lipid droplet accumulation, and the TCA cycle. Meanwhile, chemerin inhibits LDL uptake by reducing LDLR and SORT1 in trophoblasts, which leads to an increase in the release of lipids and the lipid-related protein (TG, Chol, phospholipids, and chemerin) from the placenta to maternal circulation, as well as a lower LDL uptake from circulation to placenta, eventually resulting in dyslipidemia in the patient (This figure with the credit “Created with BioRender.com.”)