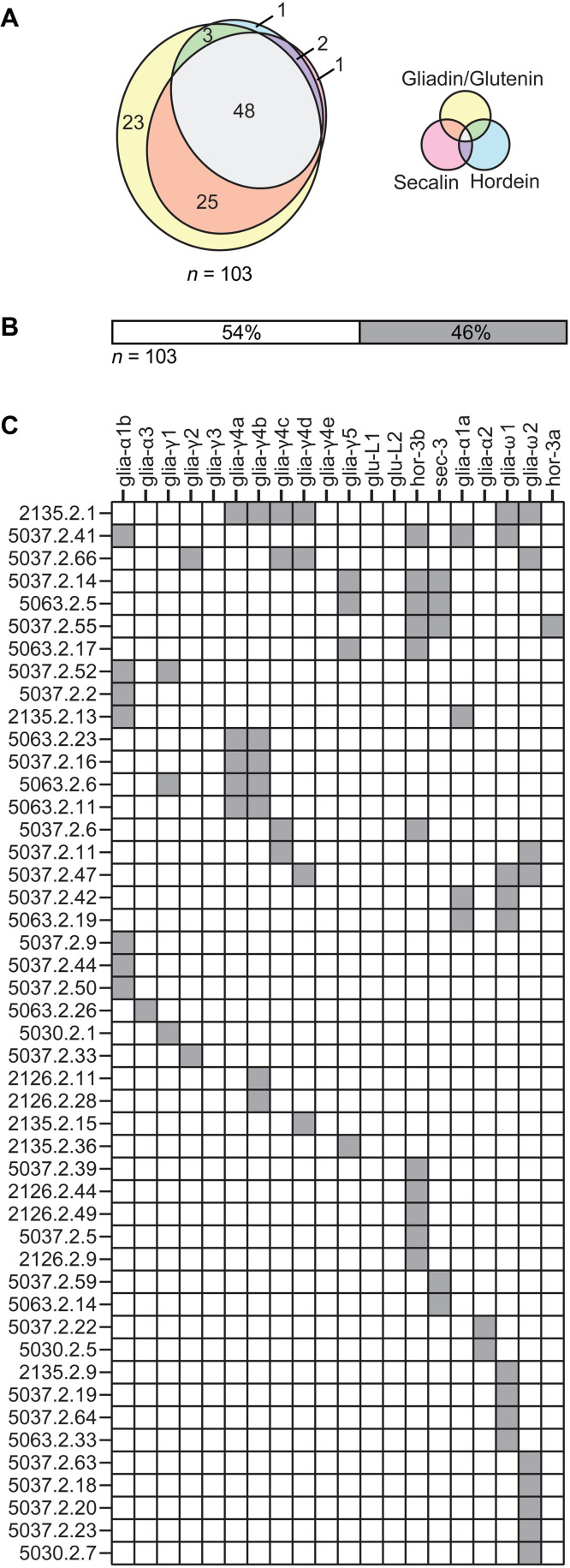
Fig. 1. Grain reactivity and epitope specificity of gluten-reactive TCCs.
(A) From 179 TCCs that carried the phenotype typical of gluten-specific T cells in CeD and that stained negative with HLA-DQ:gluten tetramers, we identified 103 TCCs that were reactive to chymotrypsin-digested and TG2-treated gliadin/glutenin, hordein, or secalin. The Venn diagram depicts the number of TCCs reactive to the respective gluten proteins. All gluten proteins were tested at a concentration of 10 μg. The TCCs that were not reactive to any of the digests are not shown. (B) Frequency of the gluten-reactive TCCs recognizing known (filled box) or unknown epitopes (n = 103) in T cell proliferation assays. (C) Epitope specificity of the gluten-reactive TCCs. The individual TCCs are indicated by numbers and the peptides are indicated by epitope names. Only TCCs that were reactive to at least one tested peptide are displayed (47 of 103) (filled boxes). All peptides were tested in T cell proliferation assays at 10 μM concentration. The TCCs were considered reactive if the stimulation index (SI) was higher than 1.8. This screening experiment that aims to select for informative TCCs was performed once in triplicate.