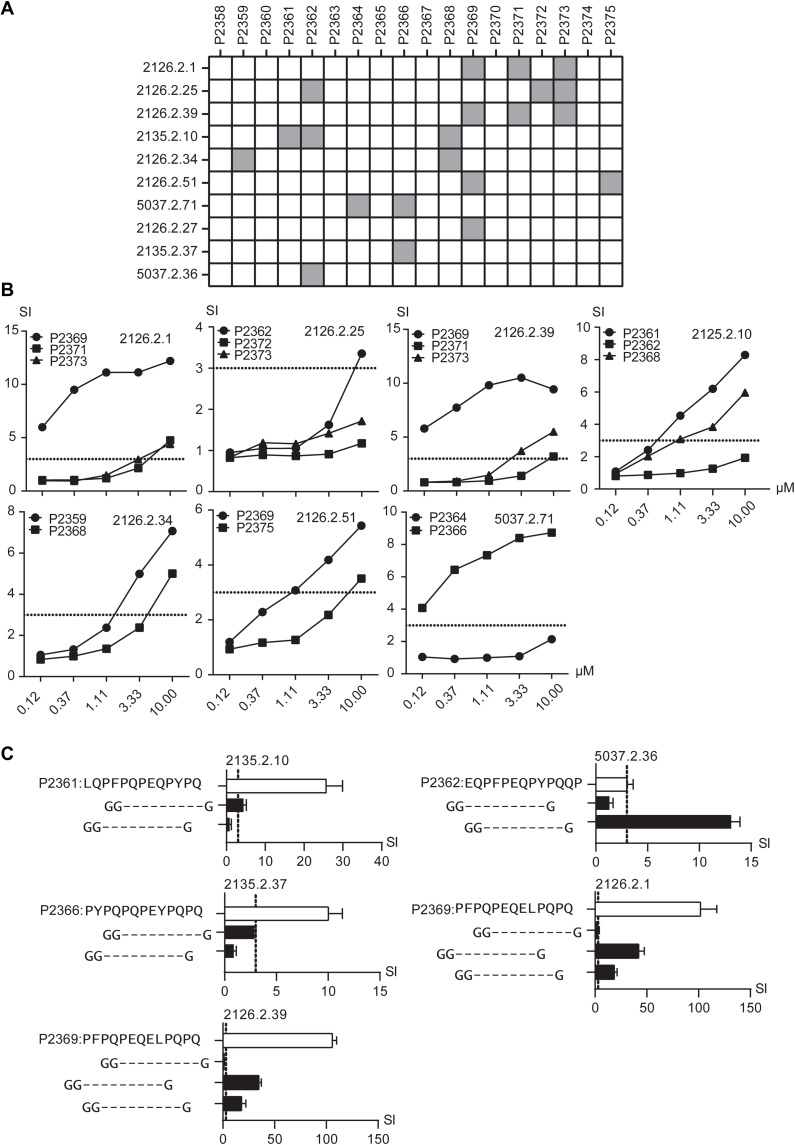
Fig. 2. Identification of five previously uncharacterized gliadin/gluten epitopes.
(A) Gliadin/glutenin-reactive TCCs (n = 42) were tested against a panel of 18 peptides in T cell proliferation assays. TCCs are indicated by numbers on the left and peptides are indicated by peptide IDs on the top (Table 1). TCCs (n = 10) that were reactive to at least one peptide are indicated as filled boxes. (B) Seven cross-reactive TCCs were examined in T cell proliferation assays with threefold titrated concentrations of the respective stimulatory peptides. (C) TCCs with previously defined stimulatory 13-nucleotide oligomer peptide sequence were tested against shorter peptides representing respective possible peptide-binding register variants flanked by two glycine residues at the N terminus and one glycine residue at the C terminus in a T cell proliferation assay. Only reactive TCCs are displayed. White bars represent original stimulatory 13-nucleotide oligomer sequences for each TCC, whereas black bars represent the reactivity to shorter peptides containing only a single possible candidate epitope sequence. TCCs reactive to at least one shorter peptide are displayed. Error bars in (C) represent SD. All peptides were tested at 10 μM concentration (unless stated otherwise) in triplicate. The TCCs were considered reactive if SI > 3 (stippled line). Results from one representative experiment of two are shown.