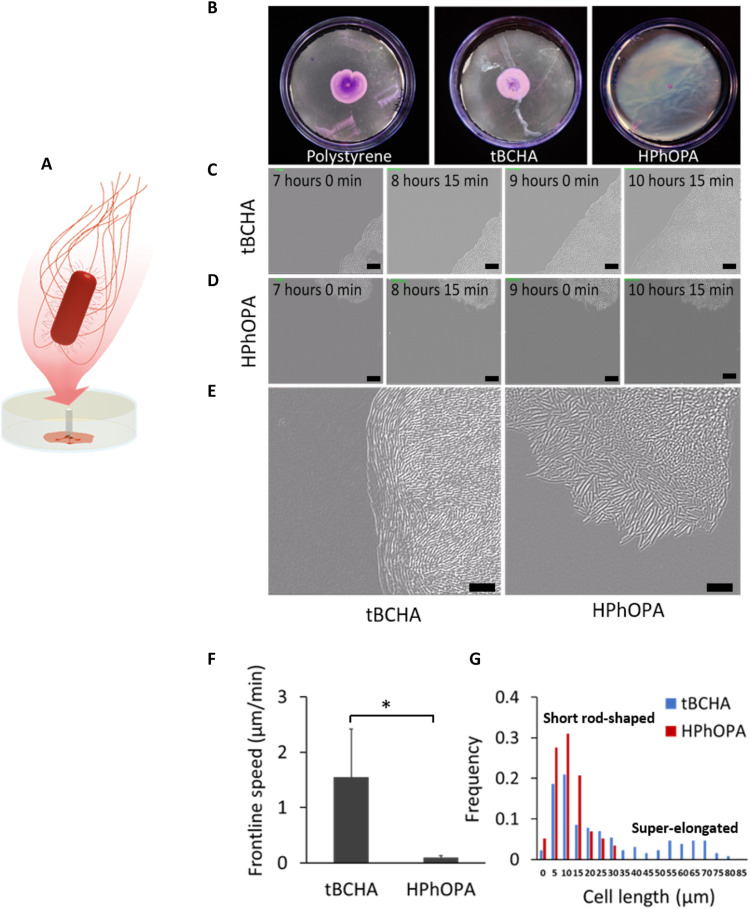
Fig. 3. Swarming characteristics of P. mirabilis during migration on tBCHA and HPhOPA.
(A) Schematic depiction of the swarming migration assay. P. mirabilis was inoculated onto an uncoated or poly(tBCHA)- or poly(HPhOPA)-coated polystyrene surfaces and incubated at 37°C for 7 hours. (B) Images of crystal violet–stained bacteria swarming between agar and, from left to right, uncoated polystyrene, tBCHA-coated, or HPhOPA-coated polystyrene. (C and D) DIC microscopy time series showing images taken every 45 min from 7 hours after inoculation and for three additional time points on (C) poly(tBCHA) and (D) poly(HPhOPA). Scale bars, 20 μm. (E) Enlarged DIC image of the swarming migration front of P. mirabilis on poly(tBCHA) (left) or poly(HPhOPA) (right) showing the elongation and alignment of bacterial cells at the moving front on poly(tBCHA) and their absence on HPhOPA. (F) Frontline speed and the cell length (G) within the cell population found on the poly(tBCHA)-coated (blue) or poly(HPhOPA)-coated (red) surfaces. Error bars in (F) are equal to ± 1 SD for at least three independent replicates. *P ≤ 0.05. Significance was determined by unpaired Student t test. Scale bars, 20 μm.