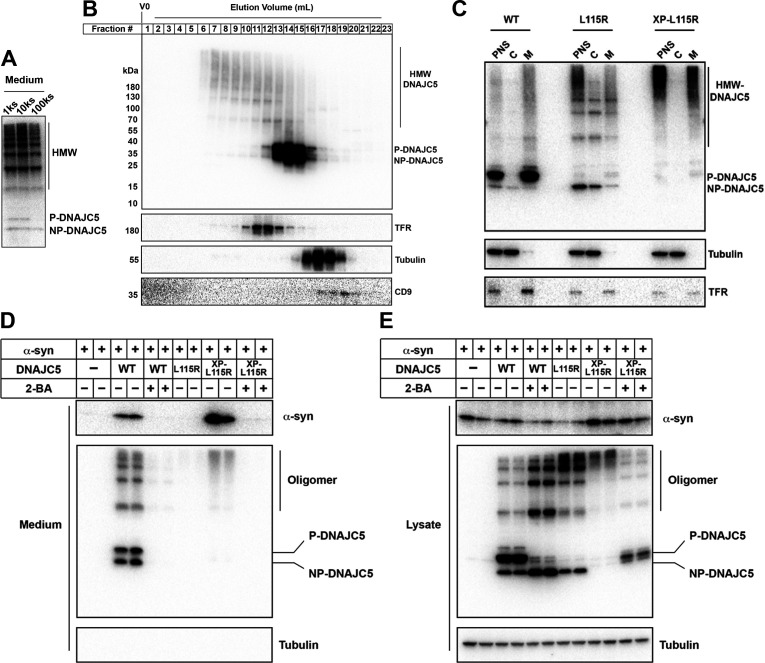
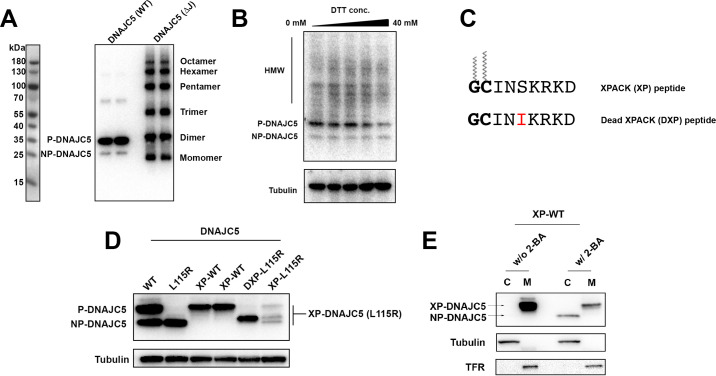
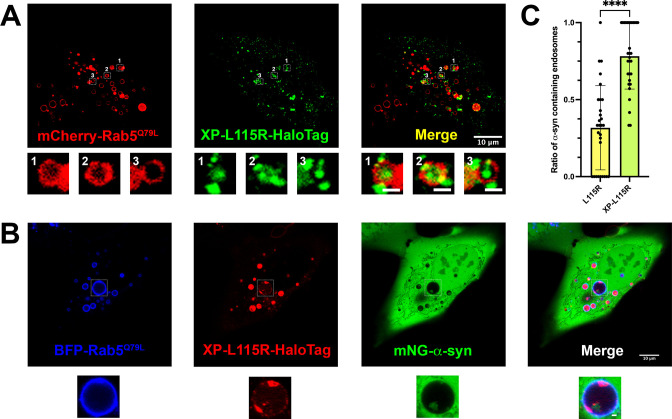
Figure 6. XPACK (XP)-induced DNAJC5 L115R oligomerization rescued α-syn secretion.
(A) Ladder pattern of higher molecular weight (HMW) DNAJC5 oligomers in the medium. Medium from HEK293T cell culture transfected with DNAJC5 was centrifuged at 1000 (1k)×g, 10,000 (10k)×g, and 100,000 (100k)×g, followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot of supernatant (s) fractions at each centrifugation step. (B) Fractionation of HMW-DNAJC5 with gel filtration. HEK293T cells transfected with DNAJC5 were lysed, clarified, and subjected to gel filtration. HMW-DNAJC5 of different sizes were separated based on their corresponding molecular weight. (C) XP-DNAJC5 L115R mutant forms a membrane-bound oligomer. Cellular fractionation was performed with HEK293T cells transfected with indicated DNAJC5 variants. Note the substantial change of electrophoretic mobility of XP-DNAJC5 L115R on SDS-PAGE. (D) α-syn secretion induced by XP-DNAJC5 L115R. Secretion assay was performed with HEK293T cells transfected with indicated plasmids. About 10 μm 2-BA was used to block induced α-syn. (E) Expression of α-syn and DNAJC5 variants in HEK293T cells. Note the substantial change in electrophoretic mobility of 2-BA-treated XP-DNAJC5 L115R on SDS-PAGE.