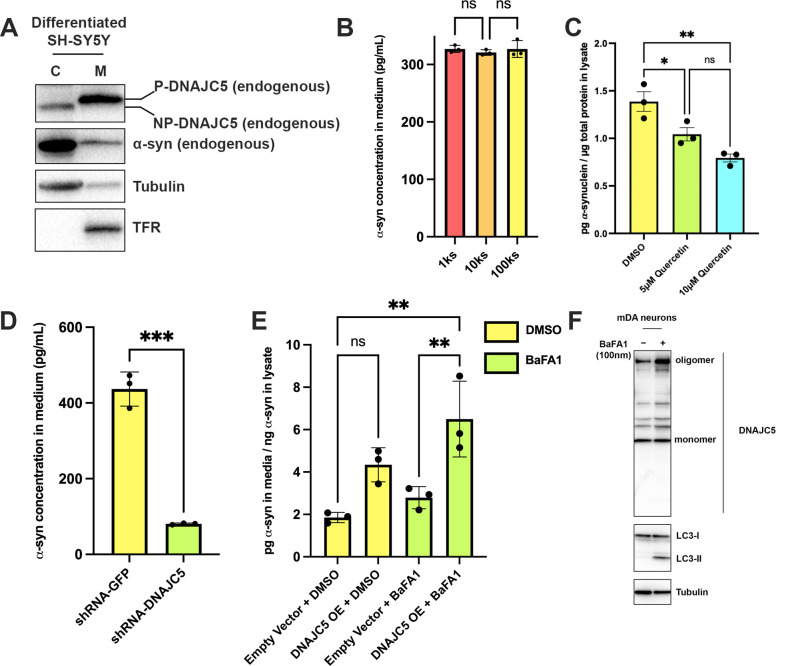
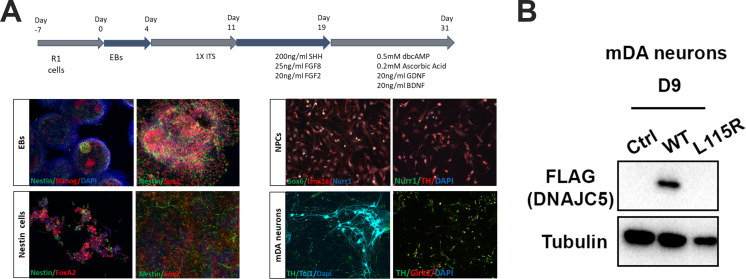
Figure 7. Recapitulation of endogenous DNAJC5-mediated α-syn secretion in various neuronal cell cultures.
(A) Membrane and cytosol fractionation of differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. The fractionation was performed as depicted in Figure 1B. C, cytosol; M, membrane. The distribution of endogenous DNAJC5 and α-syn was evaluated by immunoblot. Transferrin receptor (TFR) was used as a membrane marker. Tubulin was used as a cytosol marker. (B) Quantification of α-syn level in the supernatant of centrifuged media with ELISA. Conditioned media were collected and sequentially centrifuged at 1000 (1k)×g, 10,000 (10k)×g, and 100,000 (100k)×g. The supernatant from each centrifugation step (1ks, 10ks, and 100ks) was collected and measured by LEGEND MAX Human α-synuclein (Colorimetric) ELISA Kit. One-way ANOVA showed no significant (ns) difference of α-syn level between fractions. (C) Quercetin inhibited endogenous α-syn secretion in hiPSC-derived midbrain dopamine neurons. hiPSC-dopamine neurons carrying the GBA-N370S mutation were treated with quercetin (5 μM or 10 μM) at day 35. Culture media samples were harvested after 3 days treatment at day 38 and α-syn levels in the media were analyzed by electro-chemiluminescent immunoassay. Data points represent individual cell lines derived from different donors and are normalised to total protein in the corresponding cell lysates. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test shows a significant reduction in α-syn secretion with increasing quercetin concentration (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). (D) Depletion of endogenous DNAJC5 in SH-SY5Y cells decreased basal α-syn secretion. After 3 days of culture, the media from differentiated SH-SY5Y cells transduced with shRNA targeting GFP (shRNA-GFP) or shRNA targeting DNAJC5 (shRNA-DNAJC5) were collected and the extracellular α-syn was quantified with ELISA. P value<0.0002, two-tailed t test. (E) Expression of exogenous human DNAJC5 in mouse mDA stimulated basal α-syn secretion. WT mDA and mDA expressing hDNAJC5 were treated with DMSO or 100 nM BaFA1. Quantification of α-syn in conditioned media was performed with Mouse α-synuclein ELISA Kit (Abcam). α-syn secretion was normalized by dividing the α-syn in media (pg/ml) by the α-syn in cell lysates (ng/ml). P value<0.01, one-way ANOVA. (F) BaFA1 increased DNAJC5 oligomerization in mouse mDA neurons.