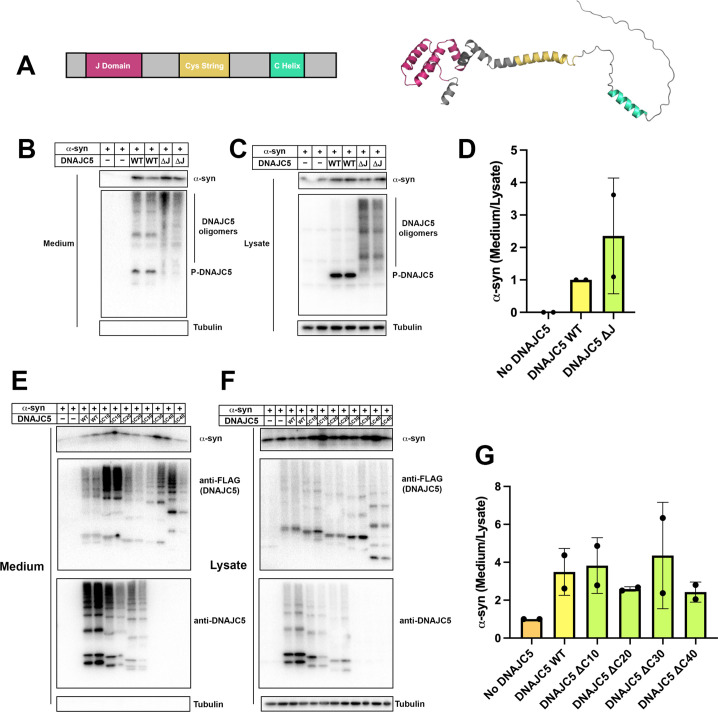
Figure 8. Domain mapping of secretion-competent DNAJC5.
(A) Predicted structure of DNAJC5 by AlphaFold. Color scheme: J domain (magenta), Cys string domain (yellow) and C-terminal helix (green). (B) DNAJC5 (ΔJ) was competent to induce α-syn secretion into the medium. HEK293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmids. Media were collected after 36 hr and evaluated with immunoblot. (C) DNAJC5 (ΔJ) formed oligomers in HEK293T cells. (D) Quantification of normalized α-syn secretion in HEK293T cells transfected with WT DNAJC5 or DNAJC5 (ΔJ). Quantification was based on immunoblot in (B) and (C). The α-syn secretion was calculated as the amount of α-syn in media divided by the amount in lysate. α-syn secretion in cells transfected with WT DNAJC5 was normalized as 1. (E) C-terminal truncated DNAJC5 constructs were competent to induce α-syn secretion in the medium. HEK293T cells were transfected with C-terminal truncated DNAJC5 and α-syn. DNAJC5 antibodies cannot recognize DNAJC5 (ΔC30) and DNAJC5 (ΔC40) because of a missing epitope in the C-terminus. Instead, DNAJC5 (ΔC30) and DNAJC5 (ΔC40) were detected by C-terminal FLAG tags. All the C-terminal truncated DNAJC5 constructs showed smear-like oligomers. (F) Expression of C-terminal truncated DNAJC5 constructs in HEK293T cells. Immunoblot of anti-FLAG antibody and anti-DNAJC5 antibody cross-validated the existence of oligomers. (G) Quantification of normalized α-syn secretion in HEK293T cells transfected with WT DNAJC5 or different C-terminal truncated DNAJC5 constructs (ΔC10, ΔC20, ΔC30, and ΔC40). Quantification was based on immunoblot in (E) and (F). The α-syn secretion was calculated as the amount of α-syn in media divided by the amount in lysate. α-syn secretion in cells without DNAJC5 transfection was normalized as 1.