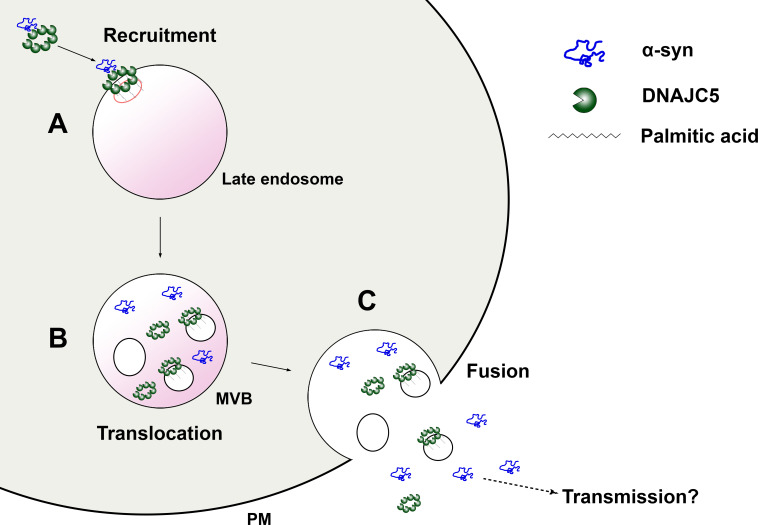
Figure 9. A model for palmitoylated DNAJC5 oligomer-mediated α-syn secretion.
(A) Recruitment of α-syn on the membrane by DNAJC5. DNAJC5 binds to α-syn and targets it to late endosomes by palmitoylation. DNAJC5 forms a high-order oligomer to accommodate α-syn. (B) Translocation of α-syn and DNAJC5 into the membrane compartment. Both α-syn and DNAJC5 are translocated into the endosome lumen along with intraluminal vesicles (ILVs), forming a multivesicular body (MVB). (C) Secretion of α-syn and DNAJC5. Upon fusion between MVB and plasma membrane (PM), the cargos are expelled into the extracellular space. α-syn is soluble. DNAJC5 exists in both soluble and membrane-bound forms. Further transmission potentially occurs after secretion.