Figure 2. Individuals with DS display chronic IGF1 deficiency downstream of GH1 production.
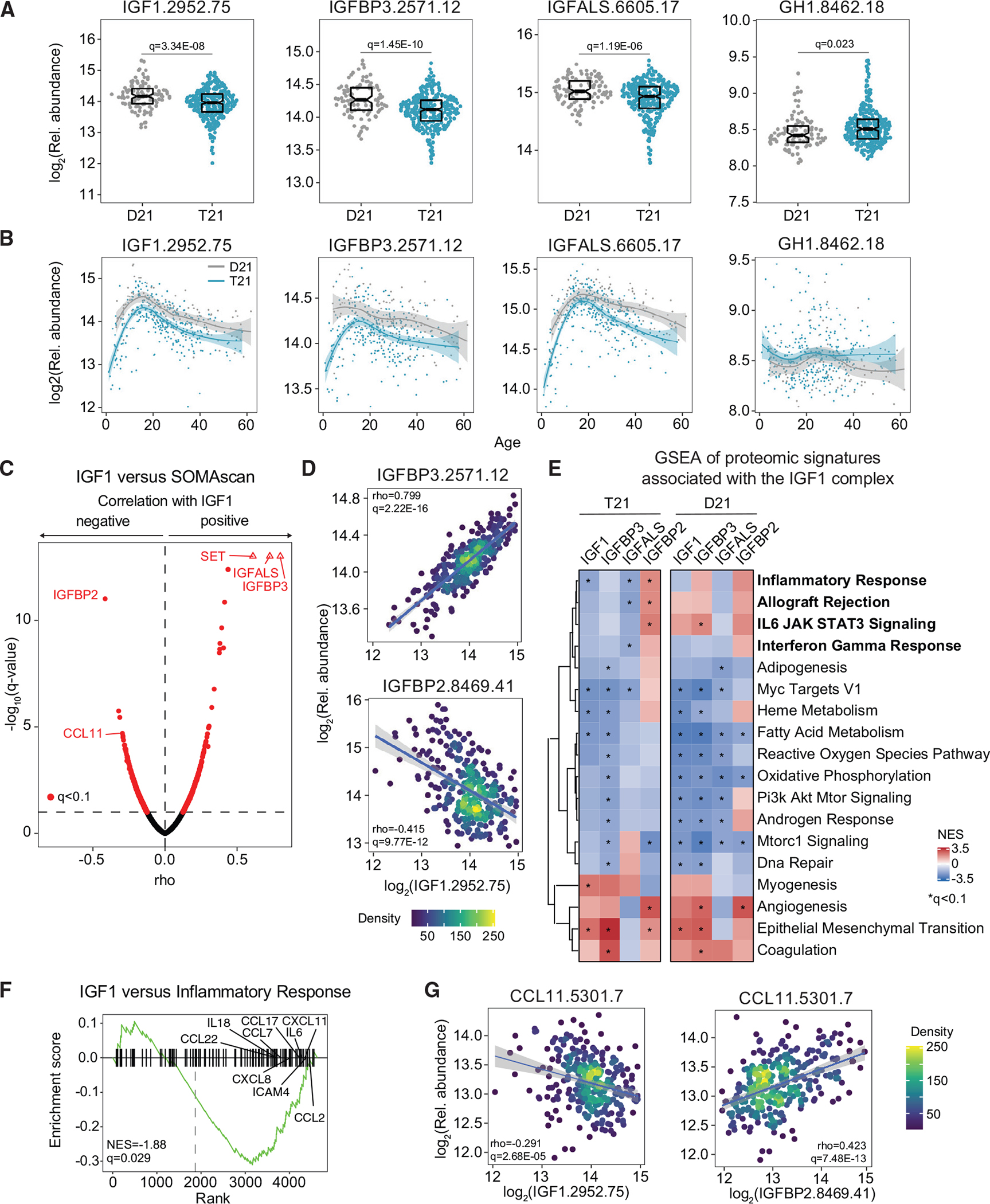
Factors in the GH1/IGF1 signaling pathway were measured in plasma samples from 419 research participants, 316 of them with T21, versus 103 age- and sex-matched euploid controls (D21).
(A) Sina plots displaying levels of IGF1, IGFBP3, IGFALS, and GH1 in individuals with and without T21. Data are presented as sina plots, with boxes indicating median and interquartile range. Differences between groups were determined with a multivariable linear regression with age, sex, and source as covariables with BH correction of p values.
(B) LOESS age trajectory plots for IGF1, IGFBP3, IGFALS, and GH1 in individuals with and without T21.
(C) Volcano plot of Spearman correlations between circulating levels of IGF1 and plasma proteins in individuals with T21.
(D) Scatterplots for levels of IGFBP3 (top) and IGFBP2 (bottom) versus IGF1 among individuals with T21. Values shown represent Spearman rho. The q values were calculated with the BH method. Points are colored by density. Lines represent a simple linear regression with 95% confidence interval.
(E) Pathways significantly enriched by normalized enrichment score (NES) from weighted gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of proteins that are significantly positively and negatively correlated with IGF1 in individuals with and without T21.
(F) Enrichment plot of the hallmark inflammatory response gene set negatively correlated with IGF1 levels in people with DS.
(G) Scatterplots for levels of CCL11 (eotaxin) protein correlated with levels of IGF1 (left) and IGFBP2 (right) among individuals with T21. Details are as in (D).
