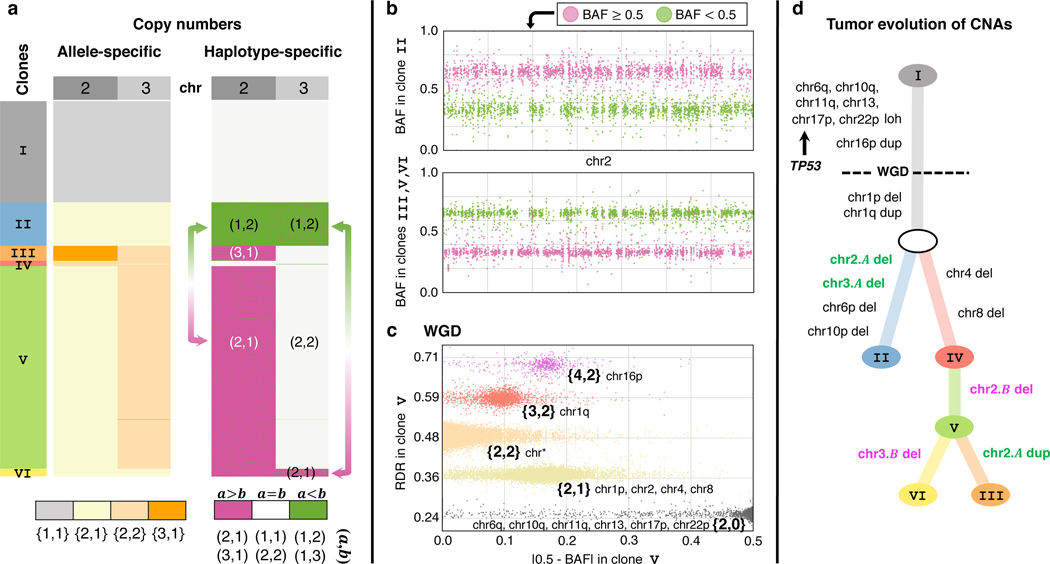
Fig. 3: CHISEL reveals haplotype-specific CNAs and WGDs that shape tumor evolution.
a, CHISEL transforms allele-specific copy numbers (left) into haplotype-specific copy numbers (right) in 1448 cells from a breast tumor (section E of patient S0). Haplotype-specific copy numbers reveal mirrored-subclonal CNAs (arrows), or CNAs that alter the two distinct alleles of the same genomic region in different cells. Here, clone II has haplotype-specific copy numbers on chromosome 2, while clones V and VI have haplotype-specific copy numbers . Similarly, clone II has haplotype-specific copy numbers on chromosome 3, while clone VI has . b, BAFs on chromosome 2 support mirrored-subclonal CNAs, with a switch in the haplotype with larger BAF between clone II and clones III, V, and VI; each point in the plot indicates BAF in a 50kb haplotype block. c, RDRs, BAFs, and allele-specific copy numbers inferred by CHISEL along the entire genome and across all cells of clone V support the occurrence of a WGD as the two standard criteria for WGD are met: the larger allele-specific copy number is greater than 2 in of the genome and most of the genome (chr*) has allele-specific copy numbers . d, A phylogenetic tree describes the CNA evolution of the 6 clones identified by CHISEL, with inferred haplotype-specific copy number events indicated on branches. LOH on multiple chromosomes and duplication of chromosome 16p precede the WGD, while deletion of chromosome 1p and duplication of chromosome 1q occur after WGD. Chromosome 17p contains the gene TP53; LOH at this locus supports published reports that TP53 inactivation precedes WGD. Mirrored-subclonal CNAs on chromosomes 2 and 3 separate the 6 clones into two clear evolutionary branches, one containing the deletions of one haplotype of chromosomes 2 and 3 and the other containing the deletions of the other haplotype. These branches are further supported by the presence of specific subclonal CNAs, affecting chromosomes 4, 6p, 8, and 10p.