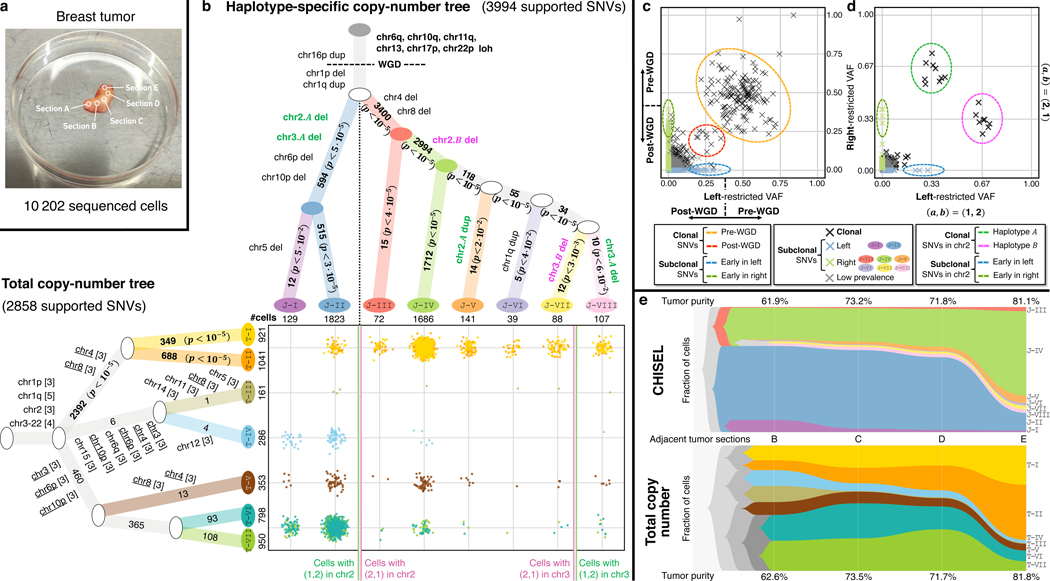
Fig. 4: Reconstruction of tumor heterogeneity and evolution across multiple tumor sections.
a, DNA from cells in five adjacent sections of a breast tumor patient S0 was sequenced using the 10x Genomics Chromium Single Cell CNV Solution in previous analysis of total copy numbers. b, Phylogenetic trees describing tumor clones and their CNA evolution as inferred by CHISEL jointly across all cells (top) and as reported in previous analysis using total copy numbers (left). Each branch of the CHISEL tree is labeled by haplotype-specific copy-number events, and each branch of the total copy number tree is labeled by total copy-number changes (in brackets with repeated events underlined). Each non-truncal branch in the trees is also labelled by the number of supported SNVs; -values comparing to the number of such SNVs expected by chance are indicated, with significant values () in boldface. Overall, 3994 SNVs support the haplotype-specific tree inferred by CHISEL, but only 2858 SNVs support the published tree inferred using total copy numbers. (Middle) Comparison of the cellular composition of clones identified in the two analyses, where each point corresponds to a cell colored by its clone assignment. For simplicity, clones T-I and T-II as well as T-VI and T-VII are merged as they are distinguished by only few isolated and small (5Mb) CNAs. Vertical lines separate cells with different haplotype-specific copy numbers in chromosomes 2 and 3 in the CHISEL tree. c, Left-restricted VAF (resp. right-restricted VAF) is computed as the VAF of SNVs using sequencing reads from cells in the left branch (clones J-1 and J-II) (resp. right branch with clones J-III ‒ J-VIII) of the CHISEL tree. Excluding low-prevalence SNVs that are potential false positives, the CHISEL tree partitions SNVs according to their clonal status (clonal or subclonal in each branch) and the restricted VAFs support this classification. Clonal SNVs have restricted VAFs consistent with their occurrence before (0.33) and after (0.33) WGD. All subclonal SNVs have restricted VAF consistent with their occurrence after WGD (0.25). Subclonal SNVs with the highest restricted VAFs (some 0.33 due to CNAs) are inferred to occur early in the evolution of these clones. d, Restricted VAFs of all clonal SNVs on chromosome 2 occurring before WGD are consistent with the distinct haplotype-specific copy numbers and in the left and right branches. SNVs on haplotype A (green circle) have left-restricted VAF 0.33 and right-restricted VAF 0.67, while SNVs on haplotype B (magenta circle) have the opposite restricted VAFs. Early SNVs in both left and right branches have restricted VAFs 0.33, which is consistent with occurrence after WGD. e, The proportions of tumor clones and the corresponding tumor purity identified by CHISEL and total copy-number analysis across the four adjacent tumor sections with highest tumor purity.