Table 1.
Treatment response of infantile spasms in CDD is worse for standard first-line medications compared to a non-CDD population from the NISC database [32].
| Treatment | CDD Treated % (N) |
NISC Treated % (N) |
CDD 14-day response % (N) |
NISC 14-day response % (N) |
CDD 1-month response % (N) |
NISC 1-month response % (N) |
CDD 3-month response % (N) |
NISC 3-month response % (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
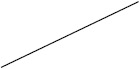
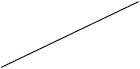
| ACTH | 38 (17/45) | 60 (225/376) | 24 (4/17) | 63 (138/219) |
|
|
0 (0/8) | 59 (128/217) |
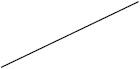
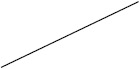
| Prednisolone | 40 (17/43) | 30 (111/376) | 12 (2/17) | 53 (51/97) |
|
|
0 (0/6) | 54 (45/84) |
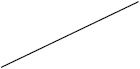
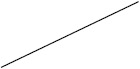
| Vigabatrin | 67 (30/45) | 53 (197/375) | 27 (7/26) | 42 (78/184) |
|
|
11 (2/19) | 42 (78/184) |
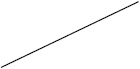
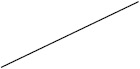
| Ketogenic diet | 53 (24/45) | 14 (51/376) |
|
|
20 (4/20) | 19 (5/27) | 17 (2/12) | 38 (15/40) |
Individuals included in the analysis had infantile spasms onset between 2 months to 2 years of age. Exclusion criteria were tuberous sclerosis complex, trisomy 21, and unknown etiology with normal development. The CDD cohort showed poorer response to all first-line treatments. Early response of the CDD cohort to ketogenic diet for refractory spasms was similar to that of the non-CDD group, but response rate was lower in the CDD cohort at 3 months [31]*. (Legend: ACTH = adrenocorticotropic hormone. CDD = CDKL5 deficiency disorder cohort. NISC = non-CDD cohort from National Infantile Spasms Consortium. * = presented at the 2020 annual American Neurological Association meeting.)
