Figure 9. Mechanisms of Dynamic and Static Obstruction in Aortic Dissection.
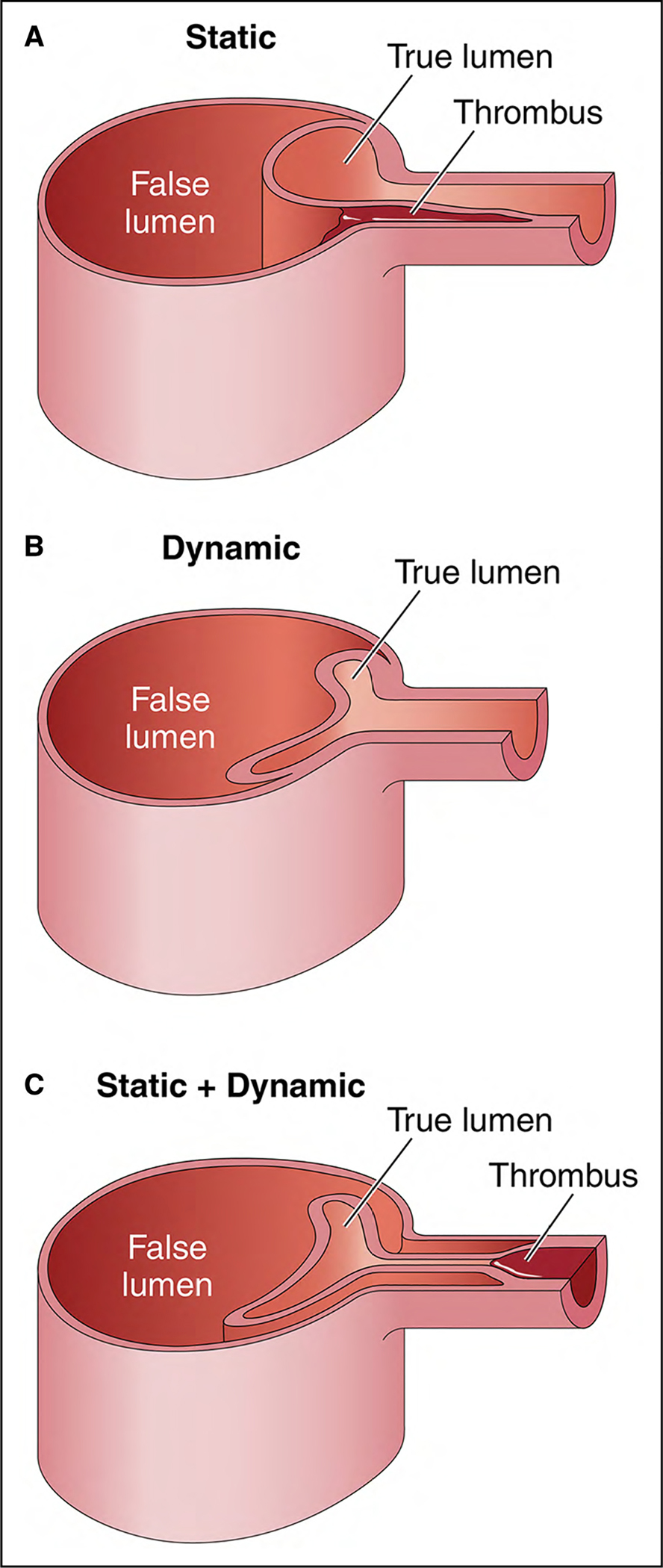
(A) Static obstruction occurs when the dissection flap extends from the aortic lumen into the ostium of the affected branch vessel, leading to localized thrombosis of the branch false lumen that narrows or colludes the branch true lumen and, consequently, impairs distal branch perfusion. (B) Dynamic obstruction occurs when the false lumen becomes persistently pressurized and compresses the true lumen, in turn pushing the dissection flap up against the ostium of the affected branch vessel, significantly reducing or occluding its flow. (C) Sometimes, a branch vessel can suffer from both static and dynamic obstruction at the same time. Adapted with permission from Grewal et al.6 Copyright 2021, Elsevier, Inc.
