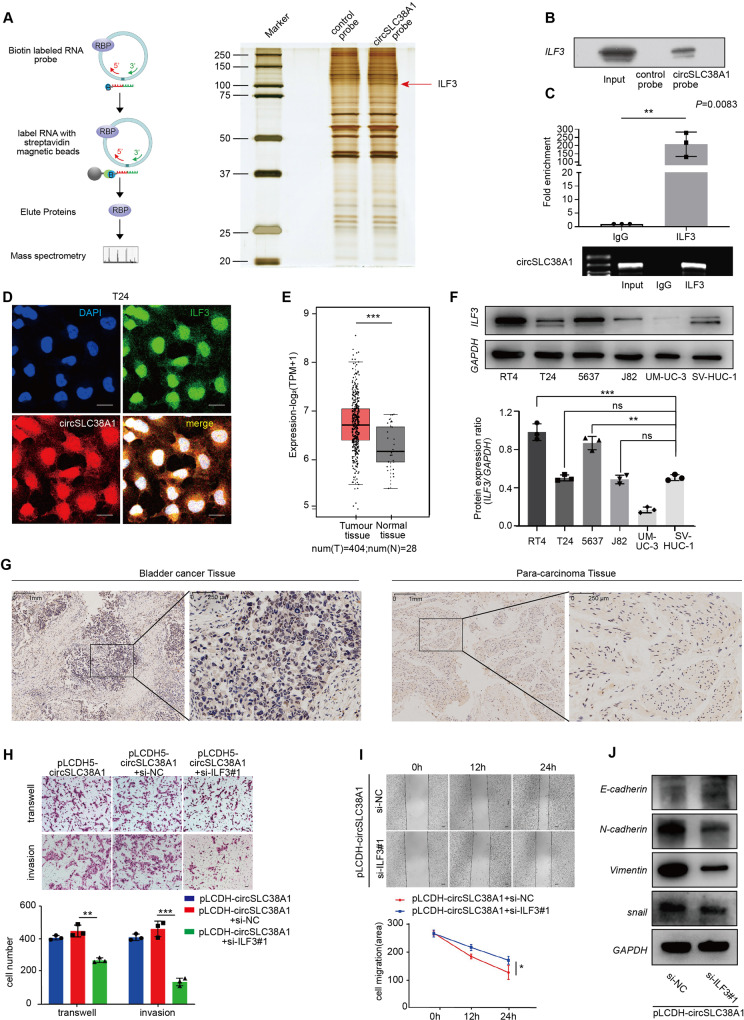
Fig. 5. CircSLC38A1 interacted with ILF3 protein.
A Left, schematic diagram showing the process of circSLC38A1-pull down. The biotin-labeled probes were used to pull down interacting proteins in T24 cells, the pull-down proteins were identified by MS. Right, identification of the circSLC38A1-protein complex pulled down by circSLC38A1 probe with protein extracts from T24 cells. The arrows indicate the additional band presented in circSLC38A1-protein complex. B Immunoblot analysis of ILF3 after pulldown assay showing its specific association with circSLC38A1. C RIP assays showing the association of ILF3 with circSLC38A1 in T24 cells. Top, fold enrichment representing RNA levels associated with ILF3 relative to IgG, IgG antibody served as a control. Bottom, agarose gel electrophoresis for products of RIP assay. D Co-localization of circSLC38A1 and ILF3 visualized by coupling circRNA FISH assay with ILF3 Immunofluorescence staining; scale bar: 25 μm. E ILF3 is up-regulated in BC based on data available from TCGA database. F Relative expression of ILF3 in BC cell lines and human normal urothelial cell line detected by western blot. G Expression levels of ILF3 in BC and adjacent normal tissues were detected by immunohistochemical staining. H, I Interference with ILF3 can effectively reverse the migratory and invasive potential of bladder cancer cells induced by circSLC38A1. J The expression levels of E-cadherin, Vimentin, ILF3, and snail between pLCDH-circSLC38A1+si-NC and pLCDH-circSLC38A1 + siILF3#1 group were detected by western blot. Data represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.