Figure 3. Intrarenal B cells have a distinct phenotype and transcriptional profile.
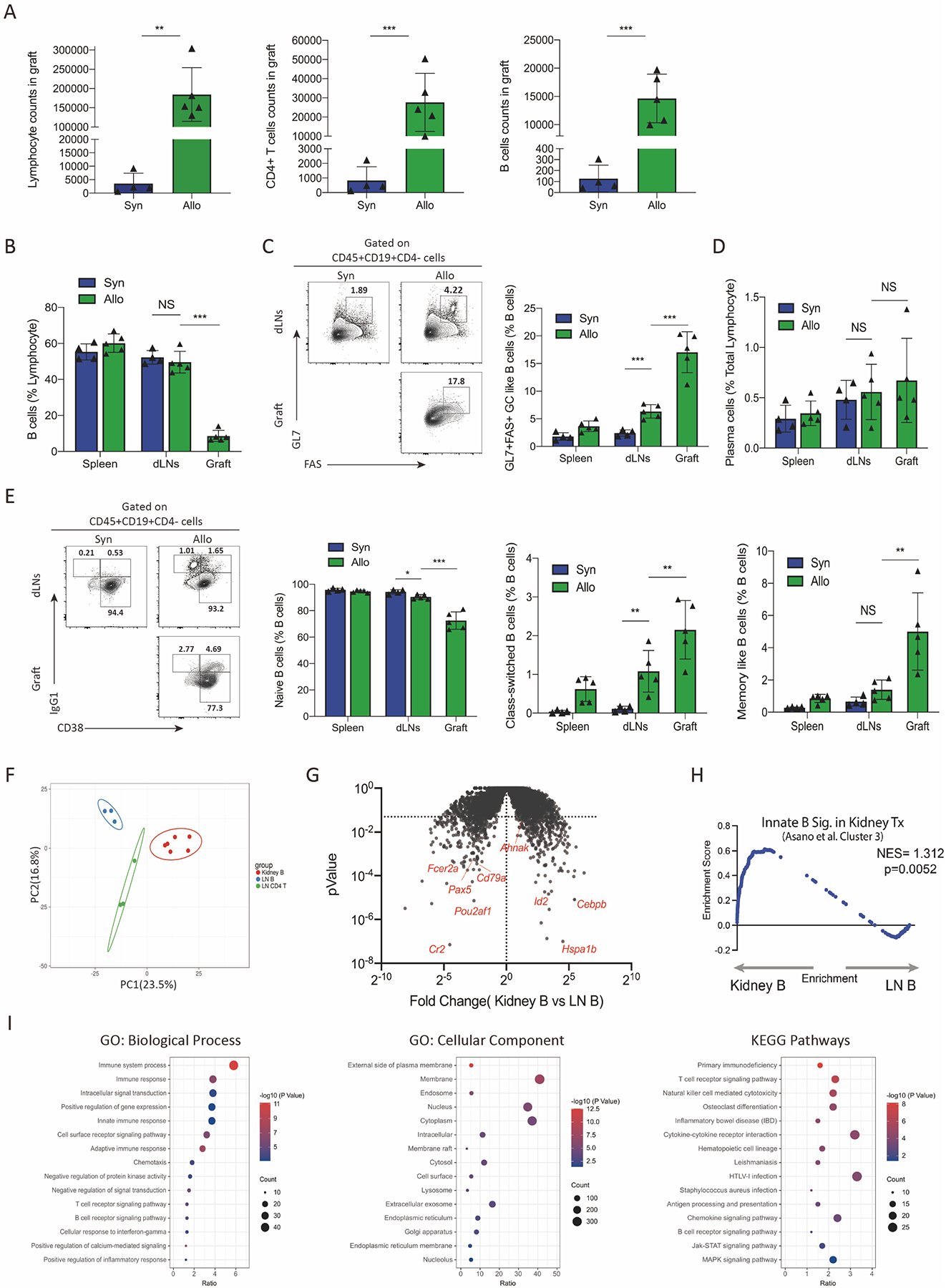
(A) Assessment of total lymphocyte count, CD45+CD4+ T cells count and CD45+CD19+ B cells count in the kidney grafts by flow cytometry. (B) Percentage of CD19+ B cells of total lymphocytes in the spleen, draining lymph nodes and grafts tissues among syngeneic and allogeneic recipients. (C) Gating strategy for GC-like B cells (gated as CD45+CD19+GL7+FAS+CD4−) and the percentage of GC-like B cells out of all CD19+B cells from different tissues. (D) Percentage of plasma cells in total lymphocytes (gated as CD45+CD138+) from spleens, dLNs and grafts. (E) Analysis of Naïve B cells (gated as CD45+CD19+CD38−IgG1−CD4−), class-switched B cells (gated as CD45+CD19+CD38−IgG1+CD4−), and memory-like B cells (CD45+CD19+CD38+IgG1+CD4−) in B cells. Representative gating (left) and quantification (right) are shown. (F) Principal component analysis (PCA) showing the relationship between transcriptional profiles of intrarenal B cells (Kidney B), dLNs B cells (LN B) and dLNs CD4+T cells (LN CD4 T) in allogeneic kidney recipients. (G) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between intrarenal B cells and dLNs B cells. Genes with P value <0.05 were considered significant. (H) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) comparing intrarenal B cells in kidney grafts to an innate-like B cell gene module (Cluster 3 from Asano et al.) (I) Enrichment of GO terms and KEGG pathways of the DEGs between intrarenal B cells and dLNs B cells. Data are from a single experiment and are representative of 3 independent repeats with n=4–5 mice per group (A-E). RNA-seq data are from combined experiments (F-I). Column graphs represent the mean with error bars indicating standard error. P value indicates 2-tailed student’s T test. NS: not significant; **: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001.
