Figure 4. Switched graft infiltrating B cells are rare but can be alloreactive.
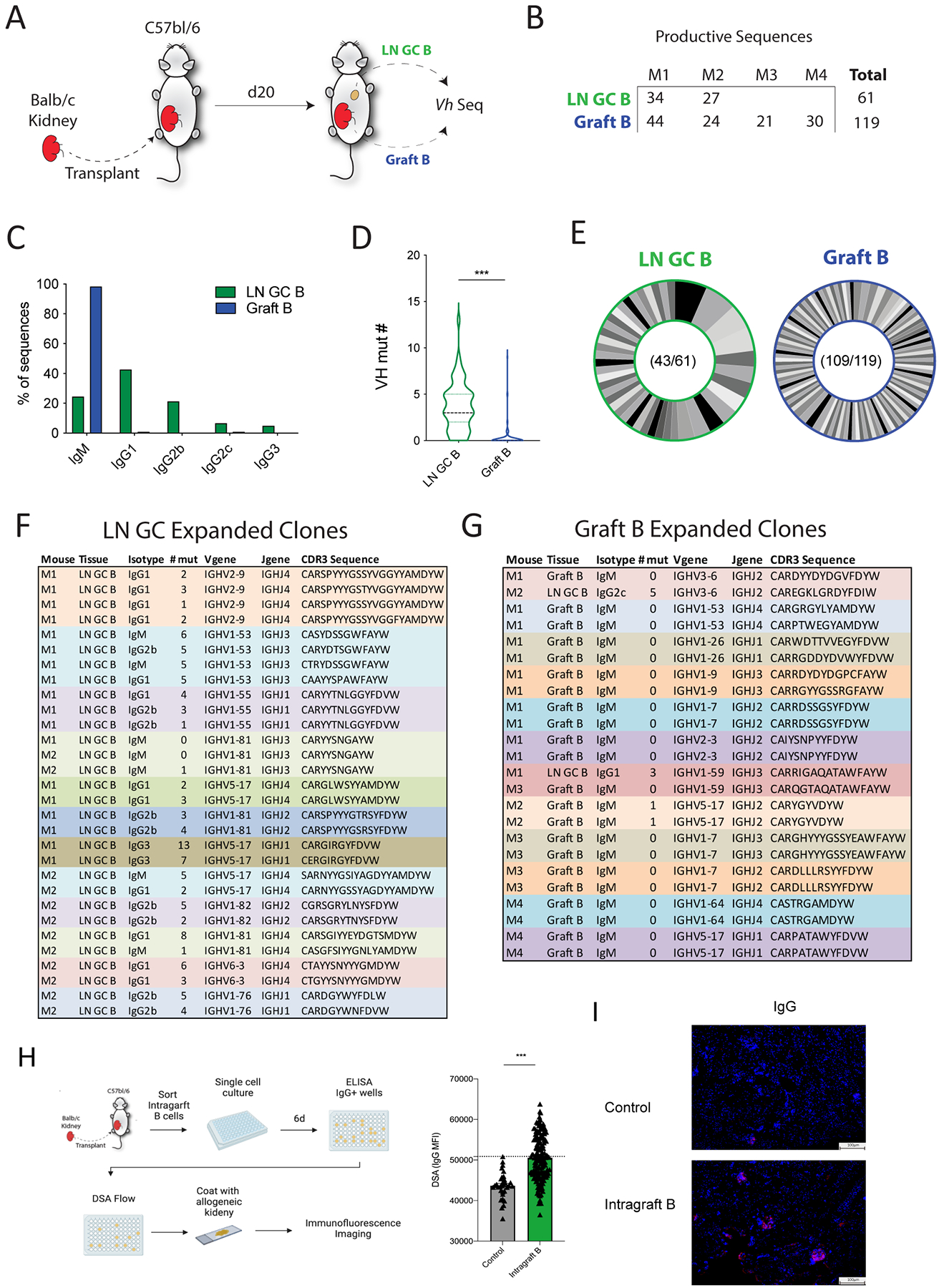
(A) Diagram of the BCR sequencing experiment. LN GC B cells (LN GC B) and intragraft B cells (Graft B) were sorted from allogeneic kidney transplant recipients on day 20 after transplantation and BCR sequencing performed. (B) Number of LN GC B cells and Graft B sequences that passed quality control cutoffs. M1: mouse 1, M2: mouse 2, M3: mouse 3, M4: mouse 4. (C) Distribution of sequences for indicated immunoglobulin isotype. (D) Somatic hypermutation analysis for V-heavy (VH) segment in LN GC B and Graft B cells. (E) Analysis of clonal distribution in B cells. Each slice indicates a unique clone. Numbers indicate the total number of clones and the number of sequences analyzed. (F, G) Details of expanded clones (sequences found 2 or more times) in dLNs GC B cells (F) and intragraft B cells (G). (H) Schematic of single B cell culture assays. Single intragraft B cells from B6 mice transplanted with a Balb/c kidney 20 days prior were cultured for 6 days with NB21 feeder cells. Culture supernatants were screened for IgG positivity, and DSA was measured in IgG switched clones. (I) Immunofluorescence staining of naïve Balb/c kidneys with pooled top 10 alloreactive clones from (H). Positive signal: red; DAPI: blue. Magnification: 100×, scale bars: 100 μm. Data are from a single experiment and are representative of 3 independent repeats Student’s 2-tailed unpaired T test, ***p<0.001.
